JavaScript API Notes
BOM
Window
const selfWindow = window.self
const topWindow = window.top
const parentWindow = window.parent
const grandParentWindow = window.parent.parent
if (confirm('Are you sure?'))
alert('I\'m so glad you\'re sure!')
else
alert('I\'m sorry to hear you\'re not sure.')
const result = prompt('What is your name? ', 'James')
if (result !== null)
alert(`Welcome, ${result}`)
// 显示打印对话框
window.print()
// 显示查找对话框
window.find()
// 显式打印机
window.print()
弹窗有非常多的安全限制:
- 禁止隐藏状态栏与地址栏.
- 弹窗默认不能移动或缩放.
- 只允许用户操作下 (鼠标/键盘) 创建弹窗.
- 屏蔽弹窗.
const newWin = window.open(
'https://www.new.com/',
'newWindow',
'height=400,width=400,top=10,left=10,resizable=yes'
)
newWin.resizeTo(500, 500)
newWin.moveTo(100, 100)
alert(newWin.opener === window) // true
newWin.close()
alert(newWin.closed) // true
let blocked = false
try {
const newWin = window.open('https://www.new.com/', '_blank')
if (newWin === null)
blocked = true
} catch (ex) {
blocked = true
}
if (blocked)
alert('The popup was blocked!')
Location
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| hash | 设置或返回从井号 (#) 开始的 URL (锚) |
| host | 设置或返回主�机名和当前 URL 的端口号 |
| hostname | 设置或返回当前 URL 的主机名 |
| href | 设置或返回完整的 URL |
| pathname | 设置或返回当前 URL 的路径部分 |
| port | 设置或返回当前 URL 的端口号 |
| protocol | 设置或返回当前 URL 的协议 |
| search | 设置或返回从问号 (?) 开始的 URL (查询部分) |
| username | 设置或返回域名前指定的用户名 |
| password | 设置或返回域名前指定的密码 |
| origin | 返回 URL 的源地址 |
function getQueryStringArgs(location) {
// 取得没有开头问号的查询字符串
const qs = location.search.length > 0 ? location.search.substring(1) : ''
// 保存数据的对象
const args = {}
// 把每个参数添加到 args 对象
for (const item of qs.split('&').map(kv => kv.split('='))) {
const name = decodeURIComponent(item[0])
const value = decodeURIComponent(item[1])
if (name.length)
args[name] = value
}
return args
}
window.location.assign('https://www.new.com')
window.location = 'https://www.new.com'
window.location.href = 'https://www.new.com'
window.location.replace('https://www.new.com') // No new history
window.location.reload() // 重新加载, 可能是从缓存加载
window.location.reload(true) // 重新加载, 从服务器加载
window.addEventListener(
'hashchange',
(event) => {
// event.oldURL
// event.nweURL
if (window.location.hash === '#someCoolFeature')
someCoolFeature()
},
false
)
Navigator
navigator 对象包含以下接口定义的属性和方法:
- NavigatorID.
- NavigatorLanguage.
- NavigatorOnLine.
- NavigatorContentUtils.
- NavigatorStorage.
- NavigatorStorageUtils.
- NavigatorConcurrentHardware.
- NavigatorPlugins.
- NavigatorUserMedia.
| Property/Method | |
|---|---|
| battery | BatteryManager (Battery Status API) |
| clipboard | Clipboard API |
| connection | NetworkInformation (Network Information API) |
| cookieEnabled | Boolean, 是否启用了 cookie |
| credentials | CredentialsContainer (Credentials Management API) |
| deviceMemory | 单位为 GB 的设备内存容量 |
| doNotTrack | 用户的不跟踪 (do-not-track) 设置 |
| geolocation | Geolocation (Geolocation API) |
| hardwareConcurrency | 设备的处理器核心数量 |
| language | 浏览器的主语言 |
| languages | 浏览器偏好的语言数组 |
| locks | LockManager (Web Locks API) |
| mediaCapabilities | MediaCapabilities (Media Capabilities API) |
| mediaDevices | 可用的媒体设备 |
| maxTouchPoints | 设备触摸屏支持的最大触点数 |
| onLine | Boolean, 表示浏览器是否联网 |
| pdfViewerEnabled | Boolean, 是否启用了 PDF 功能 |
| permissions | Permissions (Permissions API) |
| serviceWorker | ServiceWorkerContainer |
| storage | StorageManager (Storage API) |
| userAgent | 浏览器的用户代理字符串 (默认只读) |
| vendor | 浏览器的厂商名称 |
| webdriver | 浏览器当前是否被自动化程序控制 |
| xr | XRSystem (WebXR Device API) |
| registerProtocolHandler() | 将一个网站注册为特定协议的处理程序 |
| sendBeacon() | 异步传输一些小数据 |
| share() | 当前平台的原生共享机制 |
| vibrate() | 触发设备振动 |
Web Online API
const connectionStateChange = () => console.log(navigator.onLine)
window.addEventListener('online', connectionStateChange)
window.addEventListener('offline', connectionStateChange)
// 设备联网时:
// true
// 设备断网时:
// false
Web Connection API
const downlink = navigator.connection.downlink
const downlinkMax = navigator.connection.downlinkMax
const rtt = navigator.connection.rtt
const type = navigator.connection.type // wifi/bluetooth/cellular/ethernet/mixed/unknown/none.
const networkType = navigator.connection.effectiveType // 2G - 5G.
const saveData = navigator.connection.saveData // Boolean: Reduced data mode.
navigator.connection.addEventListener('change', changeHandler)
Web Protocol Handler API
navigator.registerProtocolHandler(
'mailto',
'http://www.somemailclient.com?cmd=%s',
'Some Mail Client'
)
Web Battery Status API
navigator.getBattery().then((battery) => {
// 添加充电状态变化时的处理程序
const chargingChangeHandler = () => console.log(battery.charging)
battery.addEventListener('chargingchange', chargingChangeHandler)
// 添加充电时间变化时的处理程序
const chargingTimeChangeHandler = () => console.log(battery.chargingTime)
battery.addEventListener('chargingtimechange', chargingTimeChangeHandler)
// 添加放电时间变化时的处理程序
const dischargingTimeChangeHandler = () =>
console.log(battery.dischargingTime)
battery.addEventListener(
'dischargingtimechange',
dischargingTimeChangeHandler
)
// 添加电量百分比变化时的处理程序
const levelChangeHandler = () => console.log(battery.level * 100)
battery.addEventListener('levelchange', levelChangeHandler)
})
Web Storage Estimate API
navigator.storage.estimate().then((estimate) => {
console.log(((estimate.usage / estimate.quota) * 100).toFixed(2))
})
Web Geolocation API
if (window.navigator.geolocation) {
// getCurrentPosition第三个参数为可选参数
navigator.geolocation.getCurrentPosition(locationSuccess, locationError, {
// 指示浏览器获取高精度的位置, 默认为false
enableHighAccuracy: true,
// 指定获取��地理位置的超时时间, 默认不限时, 单位为毫秒
timeout: 5000,
// 最长有效期, 在重复获取地理位置时, 此参数指定多久再次获取位置.
maximumAge: 3000,
})
} else {
alert('Your browser does not support Geolocation!')
}
locationError 为获取位置信息失败的回调函数, 可以根据错误类型提示信息:
function locationError(error) {
switch (error.code) {
case error.TIMEOUT:
showError('A timeout occurred! Please try again!')
break
case error.POSITION_UNAVAILABLE:
showError('We can\'t detect your location. Sorry!')
break
case error.PERMISSION_DENIED:
showError('Please allow geolocation access for this to work.')
break
case error.UNKNOWN_ERROR:
showError('An unknown error occurred!')
break
default:
throw new Error('Unsupported error!')
}
}
locationSuccess 为获取位置信息成功的回调函数, 返回的数据中包含经纬度等信息:
position.timestamp.position.coords:latitude: 维度.longitude: 经度.accuracy.altitude: 海拔高度.altitudeAccuracy.
结合 Google Map API 即可在地图中显示当前用户的位置信息:
function locationSuccess(position) {
const coords = position.coords
const latlng = new google.maps.LatLng(
// 维度
coords.latitude,
// 精度
coords.longitude
)
const myOptions = {
// 地图放大倍数
zoom: 12,
// 地图中心设为指定坐标点
center: latlng,
// 地图类型
mapTypeId: google.maps.MapTypeId.ROADMAP,
}
// 创建地图并输出到页面
const myMap = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById('map'), myOptions)
// 创建标记
const marker = new google.maps.Marker({
// 标注指定的经纬度坐标点
position: latlng,
// 指定用于标注的地图
map: myMap,
})
// 创建标注窗口
const infoWindow = new google.maps.InfoWindow({
content: `您在这里<br/>纬度: ${coords.latitude}<br/>经度: ${coords.longitude}`,
})
// 打开标注窗口
infoWindow.open(myMap, marker)
}
navigator.geolocation.watchPosition(
locationSuccess,
locationError,
positionOption
)
Navigator User Agent
navigator.userAgent 特别复杂:
- 历史兼容问题: Netscape -> IE -> Firefox -> Safari -> Chrome -> Edge.
- 每一个新的浏览器厂商必须保证旧网站的检测脚本能正常识别自家浏览器,
从而正常打开网页, 导致
navigator.userAgent不断变长. - UserAgent Data Parser
console.log(navigator.userAgent)
// 'Mozilla/5.0 (X11; Linux x86_64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko)
// Chrome/101.0.4922.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/101.0.1198.0'
Screen
浏览器窗口外面的客户端显示器的信息:
| Property | |
|---|---|
| availHeight | 屏幕像素高度减去系统组件高度 (只读) |
| availWidth | 屏幕像素宽度减去系统组件宽度 (只读) |
| colorDepth | 表示屏幕颜色的位数: 多数系统是 32 (只读) |
| height | 屏幕像素高度 |
| width | 屏幕像素宽度 |
| pixelDepth | 屏幕的位深 (只读) |
| orientation | Screen Orientation API 中屏幕的朝向 |
const screen = window.screen
console.log(screen.colorDepth) // 24
console.log(screen.pixelDepth) // 24
// 垂直看
console.log(screen.orientation.type) // portrait-primary
console.log(screen.orientation.angle) // 0
// 向左转
console.log(screen.orientation.type) // landscape-primary
console.log(screen.orientation.angle) // 90
// 向右转
console.log(screen.orientation.type) // landscape-secondary
console.log(screen.orientation.angle) // 270
全屏 API:
function toggleFullscreen() {
const elem = document.querySelector('video')
if (document.fullscreenElement) {
document
.exitFullscreen()
.then(() => console.log('Document Exited from Full screen mode'))
.catch(err => console.error(err))
} else {
elem
.requestFullscreen()
.then(() => {})
.catch((err) => {
alert(
`Error occurred while switch into fullscreen mode: ${err.message} (${err.name})`
)
})
}
}
document.onclick = function (event) {
if (document.fullscreenElement) {
document
.exitFullscreen()
.then(() => console.log('Document Exited from Full screen mode'))
.catch(err => console.error(err))
} else {
document.documentElement
.requestFullscreen({ navigationUI: 'show' })
.then(() => {})
.catch((err) => {
alert(
`Error occurred while switch into fullscreen mode: ${err.message} (${err.name})`
)
})
}
}
History
History Navigation
const history = window.history
// 后退一页
history.go(-1)
// 前进一页
history.go(1)
// 前进两页
history.go(2)
// 导航到最近的 new.com 页面
history.go('new.com')
// 导航到最近的 example.net 页面
history.go('example.net')
// 后退一页
history.back()
// 前进一页
history.forward()
if (history.length === 1)
console.log('这是用户窗口中的第一个页面')
if (history.scrollRestoration)
history.scrollRestoration = 'manual'
History State Management
const history = window.history
const stateObject = { foo: 'bar' }
history.pushState(stateObject, 'My title', 'baz.html')
history.replaceState({ newFoo: 'newBar' }, 'New title') // No new history state.
window.addEventListener('popstate', (event) => {
const state = event.state
if (state) {
// 第一个页面加载时状态是 null
processState(state)
}
})
Browser Compatibility
User Agent Detection
class BrowserDetector {
constructor() {
// 测试条件编译
// IE6~10 支持
this.isIE_Gte6Lte10 = /* @cc_on!@ */ false
// 测试 documentMode
// IE7~11 支持
this.isIE_Gte7Lte11 = !!document.documentMode
// 测试 StyleMedia 构造函数
// Edge 20 及以上版本支持
this.isEdge_Gte20 = !!window.StyleMedia
// 测试 Firefox 专有扩展安装 API
// 所有版本的 Firefox 都支持
this.isFirefox_Gte1 = typeof InstallTrigger !== 'undefined'
// 测试 chrome 对象及其 webstore 属性
// Opera 的某些版本有 window.chrome, 但没有 window.chrome.webstore
// 所有版本的 Chrome 都支持
this.isChrome_Gte1 = !!window.chrome && !!window.chrome.webstore
// Safari 早期版本会给构造函数的标签符追加 "Constructor"字样, 如:
// window.Element.toString(); // [object ElementConstructor]
// Safari 3~9.1 支持
this.isSafari_Gte3Lte9_1 = /constructor/i.test(window.Element)
// 推送通知 API 暴露在 window 对象上
// 使用 IIFE 默认参数值以避免对 undefined 调用 toString()
// Safari 7.1 及以上版本支持
this.isSafari_Gte7_1 = (({ pushNotification = {} } = {}) =>
pushNotification.toString() === '[object SafariRemoteNotification]')(
window.safari
)
// 测试 addons 属性
// Opera 20 及以上版本支持
this.isOpera_Gte20 = !!window.opr && !!window.opr.addons
}
isIE() {
return this.isIE_Gte6Lte10 || this.isIE_Gte7Lte11
}
isEdge() {
return this.isEdge_Gte20 && !this.isIE()
}
isFirefox() {
return this.isFirefox_Gte1
}
isChrome() {
return this.isChrome_Gte1
}
isSafari() {
return this.isSafari_Gte3Lte9_1 || this.isSafari_Gte7_1
}
isOpera() {
return this.isOpera_Gte20
}
}
Browser Feature Detection
不使用特性/浏览器推断, 往往容易推断错误 (且会随着浏览器更新产生新的错误).
// 检测浏览器是否支持 Netscape 式的插件
const hasNSPlugins = !!(navigator.plugins && navigator.plugins.length)
// 检测浏览器是否具有 DOM Level 1 能力
const hasDOM1 = !!(
document.getElementById
&& document.createElement
&& document.getElementsByTagName
)
// 特性检测
if (document.getElementById)
element = document.getElementById(id)
DOM
- DOM Level 0.
- DOM Level 1:
- DOM Core.
- DOM XML.
- DOM HTML.
- DOM Level 2:
- DOM2 Core.
- DOM2 XML.
- DOM2 HTML.
- DOM2 Views.
- DOM2 StyleSheets.
- DOM2 CSS.
- DOM2 CSS 2.
- DOM2 Events.
- DOM2 UIEvents.
- DOM2 MouseEvents.
- DOM2 MutationEvents (Deprecated).
- DOM2 HTMLEvents.
- DOM2 Range.
- DOM2 Traversal.
- DOM Level 3:
- DOM3 Core.
- DOM3 XML.
- DOM3 Events.
- DOM3 UIEvents.
- DOM3 MouseEvents.
- DOM3 MutationEvents (Deprecated).
- DOM3 MutationNameEvents.
- DOM3 TextEvents.
- DOM3 Load and Save.
- DOM3 Load and Save Async.
- DOM3 Validation.
- DOM3 XPath.
const hasXmlDom = document.implementation.hasFeature('XML', '1.0')
const hasHtmlDom = document.implementation.hasFeature('HTML', '1.0')
DOM Core
document.createElement('nodeName')
document.createTextNode('String')
document.getElementById(id)
document.getElementsByName(elementName)
document.getElementsByTagName(tagName)
document.getElementsByClassName(className) // HTML5
document.querySelector(cssSelector) // Selectors API
document.querySelectorAll(cssSelector) // Selectors API
element.getAttribute(attrName) // get default HTML attribute
element.setAttribute(attrName, attrValue)
element.removeAttribute(attrName)
element.compareDocumentPosition(element)
element.contains(element)
element.isSameNode(element) // Same node reference
element.isEqualNode(element) // Same nodeName/nodeValue/attributes/childNodes
element.matches(cssSelector)
element.closest(cssSelector) // Returns closest ancestor matching selector
element.cloneNode()
element.normalize()
element.before(...elements)
element.after(...elements)
element.replaceWith(...elements)
element.remove()
parentElement.hasChildNodes()
parentElement.appendChild(childElement)
parentElement.append(childElements)
parentElement.insertBefore(newChild, targetChild)
parentElement.replaceChild(newChild, targetChild)
parentElement.replaceChildren(children)
parentElement.removeChild(child)
function showAlert(type, message, duration = 3) {
const div = document.createElement('div')
div.className = type
div.appendChild(document.createTextNode(message))
container.insertBefore(div, form)
setTimeout(() => div.remove(), duration * 1000)
}
DOM Node Type
Node 除包括元素结点 (tag) 外,
包括许多其它结点 (甚至空格符视作一个结点),
需借助 nodeType 找出目标结点.
| Node Type | Node Representation | Node Name | Node Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ELEMENT_NODE | Tag Name | null |
| 2 | ATTRIBUTE_NODE | Attr Name | Attr Value |
| 3 | TEXT_NODE | #text | Text |
| 4 | CDATA_SECTION_NODE | #cdata-section | CDATA Section |
| 5 | ENTITY_REFERENCE_NODE | ||
| 6 | ENTITY_NODE | ||
| 8 | COMMENT_NODE | #comment | Comment |
| 9 | DOCUMENT_NODE | #document | null |
| 10 | DOCUMENT_TYPE_NODE | html/xml | null |
| 11 | DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE | #document-fragment | null |
| 12 | NOTATION_NODE |
const type = node.nodeType
const name = node.nodeName
const value = node.nodeValue
if (someNode.nodeType === Node.ELEMENT_NODE)
alert('Node is an element.')
DOM Attribute Node
const id = element.attributes.getNamedItem('id').nodeValue
const id = element.attributes.id.nodeValue
element.attributes.id.nodeValue = 'someOtherId'
const oldAttr = element.attributes.removeNamedItem('id')
element.attributes.setNamedItem(newAttr)
const attr = document.createAttribute('align')
attr.value = 'left'
element.setAttributeNode(attr)
alert(element.attributes.align.value) // "left"
alert(element.getAttributeNode('align').value) // "left"
alert(element.getAttribute('align')) // "left"
Further reading: DOM properties reflection on HTML attributes.
DOM Text Node
Text node methods:
- appendData(text): 向节点末尾添加文本 text.
- deleteData(offset, count): 从位置 offset 开始删除 count 个字符.
- insertData(offset, text): 在位置 offset 插入 text.
- replaceData(offset, count, text): 用 text 替换从位置 offset 到 offset + count 的文本.
- splitText(offset): 在位置 offset 将当前文本节点拆分为两个文本节点.
- substringData(offset, count): 提取从位置 offset 到 offset + count 的文本.
Normalize text nodes:
const element = document.createElement('div')
element.className = 'message'
const textNode = document.createTextNode('Hello world!')
const anotherTextNode = document.createTextNode('Yippee!')
element.appendChild(textNode)
element.appendChild(anotherTextNode)
document.body.appendChild(element)
alert(element.childNodes.length) // 2
element.normalize()
alert(element.childNodes.length) // 1
alert(element.firstChild.nodeValue) // "Hello world!Yippee!"
Split text nodes:
const element = document.createElement('div')
element.className = 'message'
const textNode = document.createTextNode('Hello world!')
element.appendChild(textNode)
document.body.appendChild(element)
const newNode = element.firstChild.splitText(5)
alert(element.firstChild.nodeValue) // "Hello"
alert(newNode.nodeValue) // " world!"
alert(element.childNodes.length) // 2
textContent:- Security: Doesn’t parse HTML.
- Performance: Including
<script>and<style>text content.
innerText:- Doesn't parse HTML.
- Only show human-readable text content
innerTextcare CSS styles, readinnerTextvalue will triggerreflow.
innerHTML:- Do parse HTML.
const textContent = element.textContent
const innerHTML = element.innerHTML
// eslint-disable-next-line unicorn/prefer-dom-node-text-content
const innerText = element.innerText
DOM Document Node
document node (#document):
alert(document.nodeType) // 9
alert(document.nodeName) // "#document"
alert(document.nodeValue) // null
const html = document.documentElement
const doctype = document.doctype
const head = document.head // HTML5 head.
const body = document.body
const title = document.title // 可修改.
const domain = document.domain // 可设置同源域名.
const url = document.URL
const referer = document.referer
const charSet = document.characterSet // HTML5 characterSet.
const anchors = documents.anchors
const images = documents.images
const links = documents.links
const forms = documents.forms
const formElements = documents.forms[0].elements // 第一个表单内的所有字段
// HTML5 compatMode:
if (document.compatMode === 'CSS1Compat')
console.log('Standards mode')
else if (document.compatMode === 'BackCompat')
console.log('Quirks mode')
document.getElementById(id)
document.getElementsByName(name)
document.getElementsByTagName(tagName)
document.getElementsByClassName(className) // HTML5
document.querySelector(cssSelector) // Selectors API
document.querySelectorAll(cssSelector) // Selectors API
document.write()
document.writeln()
DOM Document Type Node
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-// W3C// DTD HTML 4.01// EN" "http:// www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd">
console.log(document.doctype.name) // "html"
console.log(document.nodeType) // 10
console.log(document.doctype.nodeName) // "html"
console.log(document.doctype.nodeValue) // null
console.log(document.doctype.publicId) // "-// W3C// DTD HTML 4.01// EN"
console.log(document.doctype.systemId) // "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd"
const doctype = document.implementation.createDocumentType(
'html',
'-// W3C// DTD HTML 4.01// EN',
'http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd'
)
const doc = document.implementation.createDocument(
'http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml',
'html',
doctype
)
DOM Document Fragment Node
减少 DOM 操作次数, 减少页面渲染次数:
const frag = document.createDocumentFragment()
let p
let t
p = document.createElement('p')
t = document.createTextNode('first paragraph')
p.appendChild(t)
frag.appendChild(p)
p = document.createElement('p')
t = document.createTextNode('second paragraph')
p.appendChild(t)
frag.appendChild(p)
// 只渲染一次HTML页面
document.body.appendChild(frag)
克隆节点进行处理, 处理完毕后再替换原节点:
const oldNode = document.getElementById('result')
const clone = oldNode.cloneNode(true)
// work with the clone
// when you're done:
oldNode.parentNode.replaceChild(clone, oldNode)
Parse HTML:
const range = document.createRange()
const parse = range.createContextualFragment.bind(range)
parse(`<ol>
<li>a</li>
<li>b</li>
</ol>
<ol>
<li>c</li>
<li>d</li>
</ol>`)
function parseHTML(string) {
const context = document.implementation.createHTMLDocument()
// Set the base href for the created document so any parsed elements with URLs
// are based on the document's URL
const base = context.createElement('base')
base.href = document.location.href
context.head.appendChild(base)
context.body.innerHTML = string
return context.body.children
}
DOM Programming
Append DOM Node
| Method | Node | HTML | Text | IE | Event Listeners | Secure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| append | Yes | No | Yes | No | Preserves | Yes |
| appendChild | Yes | No | No | Yes | Preserves | Yes |
| innerHTML | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Loses | Careful |
| insertAdjacentHTML | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Preserves | Careful |
const testDiv = document.getElementById('testDiv')
const para = document.createElement('p')
testDiv.appendChild(para)
const txt = document.createTextNode('Hello World')
para.appendChild(txt)
innerHTML: non-concrete, including all types of childNodes:
div.innerHTML = '<p>Test<em>test</em>Test.</p>'
// <div>
// <p>Test<em>test</em>Test.</p>
// </div>
innerHTML performance:
// BAD
for (const value of values)
ul.innerHTML += `<li>${value}</li>` // 别这样做!
// GOOD
let itemsHtml = ''
for (const value of values)
itemsHtml += `<li>${value}</li>`
ul.innerHTML = itemsHtml
// BEST
ul.innerHTML = values.map(value => `<li>${value}</li>`).join('')
Insert DOM Node
// Append
el.appendChild(newEl)
// Prepend
el.insertBefore(newEl, el.firstChild)
// InsertBefore
el.parentNode.insertBefore(newEl, el)
// InsertAfter
function insertAfter(newElement, targetElement) {
const parent = targetElement.parentNode
if (parent.lastChild === targetElement)
parent.appendChild(newElement)
else
parent.insertBefore(newElement, targetElement.nextSibling)
}
insertAdjacentHTML/insertAdjacentText:
- beforebegin: 插入前一个兄弟节点.
- afterbegin: 插入第一个子节点.
- beforeend: 插入最后一个子节点.
- afterend: 插入下一个兄弟节点.
// 4 positions:
//
// <!-- beforebegin -->
// <p>
// <!-- afterbegin -->
// foo
// <!-- beforeend -->
// </p>
// <!-- afterend -->
const p = document.querySelector('p')
p.insertAdjacentHTML('beforebegin', '<a></a>')
p.insertAdjacentText('afterbegin', 'foo')
// simply be moved element, not copied element
p.insertAdjacentElement('beforebegin', link)
Replace DOM Node
node.replaceChild(document.createTextNode(text), node.firstChild)
node.replaceChildren(...nodeList)
Remove DOM Node
// 删除第一个子节点
const formerFirstChild = someNode.removeChild(someNode.firstChild)
// 删除最后一个子节点
const formerLastChild = someNode.removeChild(someNode.lastChild)
while (div.firstChild)
div.removeChild(div.firstChild)
// Remove self
el.parentNode.removeChild(el)
el.remove()
Traverse DOM Node
const parent = node.parentNode
const children = node.childNodes
const first = node.firstChild
const last = node.lastChild
const previous = node.previousSibling
const next = node.nextSibling
node.matches(selector)
Element Traversal API:
navigation properties listed above refer to all nodes.
For instance,
in childNodes can see both text nodes, element nodes, and even comment nodes.
const count = el.childElementCount
const parent = el.parentElement
const children = el.children
const first = el.firstElementChild
const last = el.lastElementChild
const previous = el.previousElementSibling
const next = el.nextElementSibling
el.matches(selector)
NodeList is iterable:
const elements = document.querySelectorAll('div')
for (const element of elements)
console.log(element)
const div = document.getElementById('div1')
const filter = function (node) {
return node.tagName.toLowerCase() === 'li'
? NodeFilter.FILTER_ACCEPT
: NodeFilter.FILTER_SKIP
}
const iterator = document.createNodeIterator(
div,
NodeFilter.SHOW_ELEMENT,
filter,
false
)
for (
let node = iterator.nextNode();
node !== null;
node = iterator.nextNode()
)
console.log(node.tagName) // 输出标签名
const div = document.getElementById('div1')
const walker = document.createTreeWalker(
div,
NodeFilter.SHOW_ELEMENT,
null,
false
)
walker.firstChild() // 前往<p>
walker.nextSibling() // 前往<ul>
for (
let node = walker.firstChild();
node !== null;
node = walker.nextSibling()
)
console.log(node.tagName) // 遍历 <li>
NodeFilter.acceptNode()FILTER_REJECT:- For
NodeIterator, this flag is synonymous withFILTER_SKIP. - For
TreeWalker, child nodes are also rejected.
- For
TreeWalkerhas more methods:firstChild.lastChild.previousSibling.nextSibling.
Attributes DOM Node
HTML attributes 设置对应的 DOM properties 初始值:
alert(div.getAttribute('id')) // "myDiv" default div.id
alert(div.getAttribute('class')) // "bd" default div.class
div.setAttribute('id', 'someOtherId')
div.setAttribute('class', 'ft')
div.removeAttribute('id')
div.removeAttribute('class')
// `data-src`
console.log(el.dataset.src)
Select DOM Node
startContainer: 范围起点所在的节点 (选区中第一个子节点的父节点).startOffset: 范围起点在 startContainer 中的偏移量.endContainer: 范围终点所在的节点 (选区中最后一个子节点的父节点).endOffset: 范围起点在 startContainer 中的偏移量.commonAncestorContainer: 文档中以startContainer和endContainer为后代的最深的节点.setStartBefore(refNode): 把范围的起点设置到 refNode 之前, 从而让 refNode 成为选区的第一个子节点.setStartAfter(refNode): 把范围的起点设置到 refNode 之后, 从而将 refNode 排除在选区之外, 让其下一个同胞节点成为选区的第一个子节点.setEndBefore(refNode): 把范围的终点设置到 refNode 之前, 从而将 refNode 排除在选区之外, 让其上一个同胞节点成为选区的最后一个子节点.setEndAfter(refNode): 把范围的终点设置到 refNode 之后, 从而让 refNode 成为选区的最后一个子节点.setStart(refNode, offset).setEnd(refNode, offset).deleteContents(): remove.extractContents(): remove and return.cloneContents(): clone.insertNode(node): 在范围选区的开始位置插入一个节点.surroundContents(node): 插入包含范围的内容.collapse(boolean): 范围折叠.compareBoundaryPoints(Range.HOW, sourceRange): 确定范围之间是否存在公共的边界 (起点或终点).
<!doctype html>
<html>
<body>
<p id="p1"><b>Hello</b> world!</p>
</body>
</html>
const p1 = document.getElementById('p1')
const helloNode = p1.firstChild.firstChild
const worldNode = p1.lastChild
const range = document.createRange()
range.setStart(helloNode, 2)
range.setEnd(worldNode, 3)
const fragment1 = range.cloneContents() // clone
const fragment2 = range.extractContents() // remove and return
p1.parentNode.appendChild(fragment1)
p1.parentNode.appendChild(fragment2)
const p1 = document.getElementById('p1')
const helloNode = p1.firstChild.firstChild
const worldNode = p1.lastChild
const range = document.createRange()
const span = document.createElement('span')
span.style.color = 'red'
span.appendChild(document.createTextNode('Inserted text'))
range.setStart(helloNode, 2)
range.setEnd(worldNode, 3)
range.insertNode(span)
// <p id="p1"><b>He<span style="color: red">Inserted text</span>llo</b> world</p>
const p1 = document.getElementById('p1')
const helloNode = p1.firstChild.firstChild
const worldNode = p1.lastChild
const range = document.createRange()
const span = document.createElement('span')
span.style.backgroundColor = 'yellow'
range.selectNode(helloNode)
range.surroundContents(span)
// <p><b><span style="background-color:yellow">Hello</span></b> world!</p>
Dynamic Scripts Loading
function loadScript(url) {
const script = document.createElement('script')
script.src = url
script.async = true
document.body.appendChild(script)
}
function loadScriptString(code) {
const script = document.createElement('script')
script.async = true
script.type = 'text/javascript'
try {
script.appendChild(document.createTextNode(code))
} catch (ex) {
script.text = code
}
document.body.appendChild(script)
}
所有现代浏览器中, 通过 innerHTML 属性创建的 <script> 元素永远不会执行.
Dynamic Styles Loading
function loadStyles(url) {
const link = document.createElement('link')
link.rel = 'stylesheet'
link.type = 'text/css'
link.href = url
const head = document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0]
head.appendChild(link)
}
function loadStyleString(css) {
const style = document.createElement('style')
style.type = 'text/css'
try {
style.appendChild(document.createTextNode(css))
} catch (ex) {
style.styleSheet.cssText = css
}
const head = document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0]
head.appendChild(style)
}
- 若重用同一个
<style>元素并设置该属性超过一次, 则可能导致浏览器崩溃. - 将
cssText设置为空字符串也�可能导致浏览器崩溃.
Table Manipulation
<table> 元素添加了以下属性和方法:
caption: 指向<caption>元素的指针 (如果存在).tBodies: 包含<tbody>元素的 HTMLCollection.tFoot: 指向<tfoot>元素 (如果存在).tHead: 指向<thead>元素 (如果存在).rows: 包含表示所有行的 HTMLCollection.createTHead(): 创建<thead>元素, 放到表格中, 返回引用.createTFoot(): 创建<tfoot>元素, 放到表格中, 返回引用.createCaption(): 创建<caption>元素, 放到表格中, 返回引用.deleteTHead(): 删除<thead>元素.deleteTFoot(): 删除<tfoot>元素.deleteCaption(): 删除<caption>元素.deleteRow(pos): 删除给定位置的行.insertRow(pos): 在行集合中给定位置插入一行.
<tbody> 元素添加了以下属性和方法:
rows: 包含<tbody>元素中所有行的 HTMLCollection.deleteRow(pos): 删除给定位置的行.insertRow(pos): 在行集合中给定位置插入一行, 返回该行的引用.
<tr> 元素添加了以下属性和方法:
cells: 包含<tr>元素所有表元的 HTMLCollection.deleteCell(pos): 删除给定位置的表元.insertCell(pos): 在表元集合给定位置插入一个表元, 返回该表元的引用.
// 创建表格
const table = document.createElement('table')
table.border = 1
table.width = '100%'
// 创建表体
const tbody = document.createElement('tbody')
table.appendChild(tbody)
// 创建第一行
tbody.insertRow(0)
tbody.rows[0].insertCell(0)
tbody.rows[0].cells[0].appendChild(document.createTextNode('Cell 1, 1'))
tbody.rows[0].insertCell(1)
tbody.rows[0].cells[1].appendChild(document.createTextNode('Cell 2, 1'))
// 创建第二行
tbody.insertRow(1)
tbody.rows[1].insertCell(0)
tbody.rows[1].cells[0].appendChild(document.createTextNode('Cell 1, 2'))
tbody.rows[1].insertCell(1)
tbody.rows[1].cells[1].appendChild(document.createTextNode('Cell 2, 2'))
// 把表格添加到文档主体
document.body.appendChild(table)
Iframe
| Attribute | |
|---|---|
src="https://google.com/" | Sets address of the document to embed |
srcdoc="<p>Some html</p>" | Sets HTML content of the page to show |
height="100px" | Sets iframe height in pixels |
width="100px" | Sets iframe width in pixels |
name="my-iframe" | Sets name of the iframe (used in JavaScript |
allow="fullscreen" | Sets feature policy for the iframe |
referrerpolicy="no-referrer" | Sets referrer when fetching iframe content |
sandbox="allow-same-origin" | Sets restrictions of the iframe |
loading="lazy" | Lazy loading |
<iframe src="https://www.google.com/" height="500px" width="500px"></iframe>
<iframe src="https://platform.twitter.com/widgets/tweet_button.html"></iframe>
<iframe srcdoc="<html><body>App</body></html>"></iframe>
<iframe
sandbox="allow-same-origin allow-top-navigation allow-forms allow-scripts"
src="http://maps.example.com/embedded.html"
></iframe>
const iframeDocument = iframe.contentDocument
const iframeStyles = iframe.contentDocument.querySelectorAll('.css')
iframe.contentWindow.postMessage('message', '*')
CSSOM
CSS Object Model is a set of APIs allowing the manipulation of CSS from JavaScript. It is much like the DOM, but for the CSS rather than the HTML. It allows users to read and modify CSS style dynamically.
Inline Styles
interface Element {
style: CSSStyleDeclaration
}
const style = element.style.XX
const font = element.style.fontFamily
const mt = element.style.marginTopWidth
Styles Getter and Setter
cssText: 一次生效.length.getPropertyValue(name).getPropertyPriority: return''orimportant.item(index).setProperty(name, value, priority).removeProperty(name).
const box = document.querySelector('.box')
box.style.setProperty('color', 'orange')
box.style.setProperty('font-family', 'Georgia, serif')
op.innerHTML = box.style.getPropertyValue('color')
op2.innerHTML = `${box.style.item(0)}, ${box.style.item(1)}`
box.style.setProperty('font-size', '1.5em')
box.style.item(0) // "font-size"
document.body.style.removeProperty('font-size')
document.body.style.item(0) // ""
myDiv.style.cssText = 'width: 25px; height: 100px; background-color: green'
for (let i = 0, len = myDiv.style.length; i < len; i++)
console.log(myDiv.style[i]) // 或者用 myDiv.style.item(i)
Computed Styles
- Shorthand style for full property.
- Longhand style for specific property.
getPropertyValuecan get css variables.- 在所有浏览器中计算样式都是只读的, 不能修改
getComputedStyle()方法返回的对象.
const background = window.getComputedStyle(document.body).background
// dot notation, same as above
const backgroundColor = window.getComputedStyle(el).backgroundColor
// square bracket notation
const backgroundColor = window.getComputedStyle(el)['background-color']
// using getPropertyValue()
// can get css variables property too
window.getComputedStyle(el).getPropertyValue('background-color')
CSS Class List
element.classList.add('class')
element.classList.remove('class')
element.classList.toggle('class')
element.classList.contains('class')
function addClassPolyfill(element, value) {
if (!element.className) {
element.className = value
} else {
newClassName = element.className
newClassName += ' '
newClassName += value
element.className = newClassName
}
}
DOM StyleSheets API
以下是 CSSStyleSheet 从 StyleSheet 继承的属性:
- disabled: Boolean, 表示样式表是否被禁用了 (设置为 true 会禁用样式表).
- href:
<link>URL/null. - media: 样式表支持的媒体类型集合.
- ownerNode: 指向拥有当前样式表的节点
<link>/<style>/null (@import). - title: ownerNode 的 title 属性.
- parentStyleSheet:
@importparent. - type: 样式表的类型 (
'text/css'). - cssRules: 当前样式表包含的样式规则的集合.
- ownerRule: 如果样式表是使用
@import导入的, 则指向导入规则. deleteRule(index): 在指定位置删除 cssRules 中的规则.insertRule(rule, index): 在指定位置向 cssRules 中插入规则.
CSS Rules Definition
CSSRule:
- type of
CSSRule: STYLE_RULE (1), IMPORT_RULE (3), MEDIA_RULE (4), KEYFRAMES_RULE (7). - cssText: 返回整条规则的文本.
- selectorText: 返回规则的选择符文本.
- style: 返回 CSSStyleDeclaration 对象, 可以设置和获取当前规则中的样式.
- parentRule: 如果这条规则被其他规则 (如
@media) 包含, 则指向包含规则. - parentStyleSheet: 包含当前规则的样式表.
const myRules = document.styleSheets[0].cssRules
const p = document.querySelector('p')
for (i of myRules) {
if (i.type === 1)
p.innerHTML += `<code>${i.selectorText}</code><br>`
if (i.selectorText === 'a:hover')
i.selectorText = 'a:hover, a:active'
const myStyle = i.style
// Set the bg color on the body
myStyle.setProperty('background-color', 'peachPuff')
// Get the font size of the body
myStyle.getPropertyValue('font-size')
// Get the 5th item in the body's style rule
myStyle.item(5)
// Log the current length of the body style rule (8)
console.log(myStyle.length)
// Remove the line height
myStyle.removeProperty('line-height')
// log the length again (7)
console.log(myStyle.length)
// Check priority of font-family (empty string)
myStyle.getPropertyPriority('font-family')
}
Media Rules
conditionTextproperty of media rule.- Nested
cssRules.
const myRules = document.styleSheets[0].cssRules
const p = document.querySelector('.output')
for (i of myRules) {
if (i.type === 4) {
p.innerHTML += `<code>${i.conditionText}</code><br>`
for (j of i.cssRules)
p.innerHTML += `<code>${j.selectorText}</code><br>`
}
}
Keyframe Rules
nameproperty of keyframe rulekeyTextproperty of keyframe rule.- Nested
cssRules.
const myRules = document.styleSheets[0].cssRules
const p = document.querySelector('.output')
for (i of myRules) {
if (i.type === 7) {
p.innerHTML += `<code>${i.name}</code><br>`
for (j of i.cssRules)
p.innerHTML += `<code>${j.keyText}</code><br>`
}
}
Manipulate CSS Rules
const myStylesheet = document.styleSheets[0]
console.log(myStylesheet.cssRules.length) // 8
document.styleSheets[0].insertRule(
'article { line-height: 1.5; font-size: 1.5em; }',
myStylesheet.cssRules.length
)
console.log(document.styleSheets[0].cssRules.length) // 9
const myStylesheet = document.styleSheets[0]
console.log(myStylesheet.cssRules.length) // 8
myStylesheet.deleteRule(3)
console.log(myStylesheet.cssRules.length) // 7
CSS Typed Object Model API
CSS Typed Object Model API simplifies CSS property manipulation by exposing CSS values as typed JavaScript objects rather than strings.
const styleMap = document.body.computedStyleMap()
const cssValue = styleMap.get('line-height')
const { value, unit } = cssValue
CSSKeywordValue.CSSImageValue.CSSMathValue.CSSNumericValue.CSSUnitValue.CSSTransformValue.CSSUnparsedValue.
const styleMap = document.querySelector('#myElement').attributeStyleMap
styleMap.set('display', new CSSKeywordValue('initial'))
console.log(myElement.get('display').value) // 'initial'
DOM Events
event.preventDefault().event.stopPropagation().- By default, event handlers are executed in the bubbling phase
(unless set
useCapturetotrue). element.dispatchEvent(event)to trigger events.
Events Object
| Property/Method | Type | |
|---|---|---|
| type | String | 被触发的事件类型 |
| trusted | Boolean | 浏览器生成/JavaScript 创建 |
| View | AbstractView | 事件所发生的 window 对象 |
| currentTarget | Element | Event handler binding |
| target | Element | Event trigger |
| bubbles | Boolean | 事件是否冒泡 |
| cancelable | Boolean | 是否可以取消事件的默认行为 |
| eventPhase | Number | 捕获阶段/到达目标/冒泡阶段 |
| defaultPrevented | Boolean | preventDefault() called |
| preventDefault() | Function | 用于取消事件的默认行为 |
| stopPropagation() | Function | 用于取消所有后续事件捕获或冒泡 |
| stopImmediatePropagation() | Function | 用于取消所有后续事件捕获或冒泡 |
Events Checking
function handleEvent(event) {
node.matches(event.target) // return false or true
node.contains(event.target) // return false or true
}
Global UI Events
DOMContentLoaded event:
- 当文档中没有脚本时, 浏览器解析完
HTML文档便能触发DOMContentLoaded事件. - 如果文档中包含脚本, 则脚本会阻塞文档的解析,
脚本需要等
CSSOM构建完成才能执行:- 在
DOM/CSSOM构建完毕,async脚本执行完成之后,DOMContentLoaded事件触发. HTML文档构建不受defer脚本影响, 不需要等待defer脚本执行与样式表加载,HTML解析完毕后,DOMContentLoaded立即触发.
- 在
- 在任何情况下,
DOMContentLoaded的触发不需要等待图片等其他资源加载完成. - 当
HTML文档解析完成就会触发DOMContentLoaded, 所有资源加载完成之后, load 事件才会被触发.
function ready(fn) {
if (document.readyState !== 'loading')
fn()
else
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', fn)
}
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', (event) => {
console.log('DOM fully loaded and parsed.')
})
readystatechange event:
document.addEventListener('readystatechange', (event) => {
// HTML5 readyState
if (
document.readyState === 'interactive'
|| document.readyState === 'complete'
) {
console.log('Content loaded')
} else if (document.readyState === 'loading') {
console.log('Loading')
}
})
load event (加载完成):
window.addEventListener('load', () => {
const image = document.createElement('img')
image.addEventListener('load', (event) => {
console.log(event.target.src)
})
document.body.appendChild(image)
image.src = 'smile.gif'
const script = document.createElement('script')
script.addEventListener('load', (event) => {
console.log('Loaded')
})
script.src = 'example.js'
script.async = true
document.body.appendChild(script)
const link = document.createElement('link')
link.type = 'text/css'
link.rel = 'stylesheet'
link.addEventListener('load', (event) => {
console.log('css loaded')
})
link.href = 'example.css'
document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0].appendChild(link)
})
visibilitychange event, 切换标签页时改变网页标题/声音/视频:
window.addEventListener('visibilitychange', () => {
switch (document.visibilityState) {
case 'hidden':
console.log('Tab隐藏')
break
case 'visible':
console.log('Tab被聚焦')
break
default:
throw new Error('Unsupported visibility!')
}
})
const videoElement = document.getElementById('videoElement')
// AutoPlay the video if application is visible
if (document.visibilityState === 'visible')
videoElement.play()
// Handle page visibility change events
function handleVisibilityChange() {
if (document.visibilityState === 'hidden')
videoElement.pause()
else
videoElement.play()
}
document.addEventListener('visibilitychange', handleVisibilityChange, false)
pageshow event (e.g BFCache compatible):
window.addEventListener('pageshow', (event) => {
if (event.persisted)
console.log('Page was loaded from cache.')
})
beforeunloadevent.unloadevent: 卸载完成.abortevent: 提前终止.errorevent.selectevent: 在文本框 (<input>或textarea) 上选择字符.resizeevent: 缩放.scrollevent: 滚动.
Form Events
submit/resetevent.- FromData API
- CheckValidity API
// <form className='validated-form' noValidate onSubmit={onSubmit}>
function onSubmit(event) {
event.preventDefault()
const form = event.target
const isValid = form.checkValidity() // returns true or false
const formData = new FormData(form)
const validationMessages = Array.from(formData.keys()).reduce((acc, key) => {
acc[key] = form.elements[key].validationMessage
return acc
}, {})
setErrors(validationMessages)
console.log({
validationMessages,
data,
isValid,
})
if (isValid) {
// here you do what you need to do if is valid
const data = Array.from(formData.keys()).reduce((acc, key) => {
acc[key] = formData.get(key)
return acc
}, {})
} else {
// apply invalid class
Array.from(form.elements).forEach((i) => {
if (i.checkValidity()) {
// field is valid
i.parentElement.classList.remove('invalid')
} else {
// field is invalid
i.parentElement.classList.add('invalid')
console.log(i.validity)
}
})
}
}
document.querySelector('form').addEventListener('submit', (event) => {
const form = event.target
const url = new URL(form.action || window.location.href)
const formData = new FormData(form)
const searchParameters = new URLSearchParams(formData)
const options = {
method: form.method,
}
if (options.method === 'post') {
// Modify request body to include form data
options.body
= form.enctype === 'multipart/form-data' ? formData : searchParameters
} else {
// Modify URL to include form data
url.search = searchParameters
}
fetch(url, options)
event.preventDefault()
})
import { useRouter } from 'next/navigation'
export default function Page() {
const router = useRouter()
const handleSubmit = (event) => {
event.preventDefault()
const formData = new FormData(event.target)
const data = Object.fromEntries(formData)
// Do something with data. Most likely, send it to the server using fetch
// Redirect the user to the new page
router.push('/thank-you')
}
return <form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>...</form>
}
Input Events
blur/focus/focusin/focusoutevent.input/changeevent.selectevent: 在文本框 (<input>或textarea) 上选择字符.compositionevent: 中文输入事件.
Input Focus Event
HTML5 focus management:
- 在页面完全加载之前,
document.activeElement为 null. - 默认情况下,
document.activeElement在页面刚加载完之后会设置为document.body.
document.getElementById('myButton').focus()
console.log(document.activeElement === button) // true
console.log(document.hasFocus()) // true
当焦点从页面中的一个元素移到另一个元素上时, 会依次发生如下事件:
focusout: 在失去焦点的元素上触发.focusin: 在获得焦点的元素上触发blur: 在失去焦点的元素上触发DOMFocusOut: 在失去焦点的元素上触发focus: 在获得焦点的元素上触发DOMFocusIn: 在获得焦点的元素上触发.
Input Change Event
inputevent:<input type="text" />.<input type="password"/>.<textarea />.
changeevent:<input type="checkbox" />.<input type="radio" />.<input type="file" />.<input type="file" multiple />.<select />.
const input = document.querySelector('input')
input.addEventListener('change', () => {
for (const file of Array.from(input.files)) {
const reader = new FileReader()
reader.addEventListener('load', () => {
console.log('File', file.name, 'starts with', reader.result.slice(0, 20))
})
reader.readAsText(file)
}
})
Input Select Event
const input = document.querySelector('input')
input.addEventListener('select', (event) => {
const log = document.getElementById('log')
const selection = event.target.value.substring(
event.target.selectionStart,
event.target.selectionEnd
)
log.textContent = `You selected: ${selection}`
})
Clipboard Events
Clipboard API
(modern alternative for document.execCommand(command)):
copyevent.cutevent.pasteevent.
const source = document.querySelector('div.source')
source.addEventListener('copy', (event) => {
const selection = document.getSelection()
event.clipboardData.setData(
'text/plain',
selection.toString().concat('copyright information')
)
event.preventDefault()
})
Mouse Events
mousedownevent.mouseupevent.clickevent:mousedown与mouseup都触发后, 触发此事件.event.clientX/event.clientY.event.pageX/event.pageY.event.screenX/event.screenY.event.shiftKey/event.ctrlKey/event.altKey/event.metaKey.
dbclickevent:click两次触发后, 触发此事件.mousemoveevent.mouseenterevent.mouseleaveevent: pointer has exited the element and all of its descendants.mouseoutevent: pointer leaves the element or leaves one of the element's descendants.mouseoverevent.wheelevent (replace deprecatedmousewheelevent).
For click event, no need for X/Y to judge internal/outside state.
Use element.contains to check is a better way.
window.addEventListener('click', (event) => {
if (document.getElementById('main').contains(event.target))
process()
})
- dragstart: start point.
- dragend
- dragenter: call
event.preventDefault()in drop zone. - dragover: call
event.preventDefault()in drop zone. - dragleave
- drop: end point.
Key point for implementing DnD widget is DataTransfer:
- Bindings between Drag Zone and Drop Zone.
DataTransfer.dropEffectandDataTransfer.effectAllowedto define DnD UI type.DataTransfer.getDataandDataTransfer.setDatato transfer data.DataTransfer.filesandDataTransfer.itemsto transfer data.
const noContext = document.getElementById('noContextMenu')
noContext.addEventListener('contextmenu', (e) => {
e.preventDefault()
})
Keyboard Events
keydown/keypress/keyup event:
const textbox = document.getElementById('myText')
textbox.addEventListener('keyup', (event) => {
console.log(event.charCode || event.keyCode)
})
event.key
(replace deprecated event.keyCode):
'Alt'
'CapsLock'
'Control'
'Fn'
'Numlock'
'Shift'
'Enter'
'Tab'
' ' // space bar
'ArrowDown'
'ArrowLeft'
'ArrowRight'
'ArrowUp'
'Home'
'End'
'PageDOwn'
'PageUp'
'Backspace'
'Delete'
'Redo'
'Undo'
Device Events
deviceorientationevent.devicemotionevent.touchstartevent.touchmoveevent.touchendevent.touchcancelevent.
Use
touch
events:
- Dispatch custom
tap/press/swipe/pinch/drag/drop/rotateevent. - Dispatch standard
click/dbclick/mousedown/mouseup/mousemove` event.
interface Pointer {
startTouch: Touch
startTime: number
status: string
element: TouchEventTarget
lastTouch?: Touch
lastTime?: number
deltaX?: number
deltaY?: number
duration?: number
distance?: number
isVertical?: boolean
}
type TouchEventTarget = HTMLDivElement | EventTarget
type TouchEventHandler = (pointer: Pointer, touch: Touch) => void
class Recognizer {
pointers: Map<Touch['identifier'], Pointer>
constructor() {
this.pointers = new Map()
}
start(event: TouchEvent, callback?: TouchEventHandler) {
// touches: 当前屏幕上所有触摸点的列表.
// targetTouches: 当前对象上所有触摸点的列表.
// changedTouches: 涉及当前事件的触摸点的列表.
for (let i = 0; i < event.changedTouches.length; i++) {
const touch = event.changedTouches[i]
const pointer: Pointer = {
startTouch: touch,
startTime: Date.now(),
status: 'tapping',
element: event.target,
}
this.pointers.set(touch.identifier, pointer)
if (callback)
callback(pointer, touch)
}
}
move(event: TouchEvent, callback?: TouchEventHandler) {
for (let i = 0; i < event.changedTouches.length; i++) {
const touch = event.changedTouches[i]
const pointer = this.pointers.get(touch.identifier)
if (!pointer)
return
if (!pointer.lastTouch) {
pointer.lastTouch = pointer.startTouch
pointer.lastTime = pointer.startTime
pointer.deltaX = 0
pointer.deltaY = 0
pointer.duration = 0
pointer.distance = 0
}
let time = Date.now() - pointer.lastTime
if (time > 0) {
const RECORD_DURATION = 70
if (time > RECORD_DURATION)
time = RECORD_DURATION
if (pointer.duration + time > RECORD_DURATION)
pointer.duration = RECORD_DURATION - time
pointer.duration += time
pointer.lastTouch = touch
pointer.lastTime = Date.now()
pointer.deltaX = touch.clientX - pointer.startTouch.clientX
pointer.deltaY = touch.clientY - pointer.startTouch.clientY
const x = pointer.deltaX * pointer.deltaX
const y = pointer.deltaY * pointer.deltaY
pointer.distance = Math.sqrt(x + y)
pointer.isVertical = x < y
if (callback)
callback(pointer, touch)
}
}
}
end(event: TouchEvent, callback?: TouchEventHandler) {
for (let i = 0; i < event.changedTouches.length; i++) {
const touch = event.changedTouches[i]
const id = touch.identifier
const pointer = this.pointers.get(id)
if (!pointer)
continue
if (callback)
callback(pointer, touch)
this.pointers.delete(id)
}
}
cancel(event: TouchEvent, callback?: TouchEventHandler) {
this.end(event, callback)
}
fire(elem: TouchEventTarget, type: string, props: EventInit) {
if (elem) {
const event = new Event(type, {
bubbles: true,
cancelable: true,
...props,
})
elem.dispatchEvent(event)
}
}
static bind(el: TouchEventTarget, recognizer: Recognizer) {
function move(event: TouchEvent) {
recognizer.move(event)
}
function end(event: TouchEvent) {
recognizer.end(event)
document.removeEventListener('touchmove', move)
document.removeEventListener('touchend', end)
document.removeEventListener('touchcancel', cancel)
}
function cancel(event: TouchEvent) {
recognizer.cancel(event)
document.removeEventListener('touchmove', move)
document.removeEventListener('touchend', end)
document.removeEventListener('touchcancel', cancel)
}
el.addEventListener('touchstart', (event: TouchEvent) => {
recognizer.start(event)
document.addEventListener('touchmove', move)
document.addEventListener('touchend', end)
document.addEventListener('touchcancel', cancel)
})
}
}
export default Recognizer
Dispatch Events
Dispatch MouseEvent:
const btn = document.getElementById('myBtn')
// 创建 event 对象
const event = new MouseEvent('click', {
bubbles: true,
cancelable: true,
view: document.defaultView,
})
// 触发事件
btn.dispatchEvent(event)
Dispatch KeyboardEvent:
const textbox = document.getElementById('myTextbox')
// 按照 DOM3 的方式创建 event 对象
if (document.implementation.hasFeature('KeyboardEvents', '3.0')) {
// 初始化 event 对象
const event = new KeyboardEvent('keydown', {
bubbles: true,
cancelable: true,
view: document.defaultView,
key: 'a',
location: 0,
shiftKey: true,
})
// 触发事件
textbox.dispatchEvent(event)
}
Dispatch CustomEvent:
const div = document.getElementById('myDiv')
div.addEventListener('myEvent', (event) => {
console.log(`DIV: ${event.detail}`)
})
document.addEventListener('myEvent', (event) => {
console.log(`DOCUMENT: ${event.detail}`)
})
if (document.implementation.hasFeature('CustomEvents', '3.0')) {
const event = new CustomEvent('myEvent', {
bubbles: true,
cancelable: true,
detail: 'Hello world!',
})
div.dispatchEvent(event)
}
Events Util
class EventUtil {
static getEvent(event) {
return event || window.event
}
static getTarget(event) {
return event.target || event.srcElement
}
static getRelatedTarget(event) {
// For `mouseover` and `mouseout` event:
if (event.relatedTarget)
return event.relatedTarget
else if (event.toElement)
return event.toElement
else if (event.fromElement)
return event.fromElement
else
return null
}
static preventDefault(event) {
if (event.preventDefault)
event.preventDefault()
else
event.returnValue = false
}
static stopPropagation(event) {
if (event.stopPropagation)
event.stopPropagation()
else
event.cancelBubble = true
}
static addHandler(element, type, handler) {
if (element.addEventListener)
element.addEventListener(type, handler, false)
else if (element.attachEvent)
element.attachEvent(`on${type}`, handler)
else
element[`on${type}`] = handler
}
static removeHandler(element, type, handler) {
if (element.removeEventListener)
element.removeEventListener(type, handler, false)
else if (element.detachEvent)
element.detachEvent(`on${type}`, handler)
else
element[`on${type}`] = null
}
}
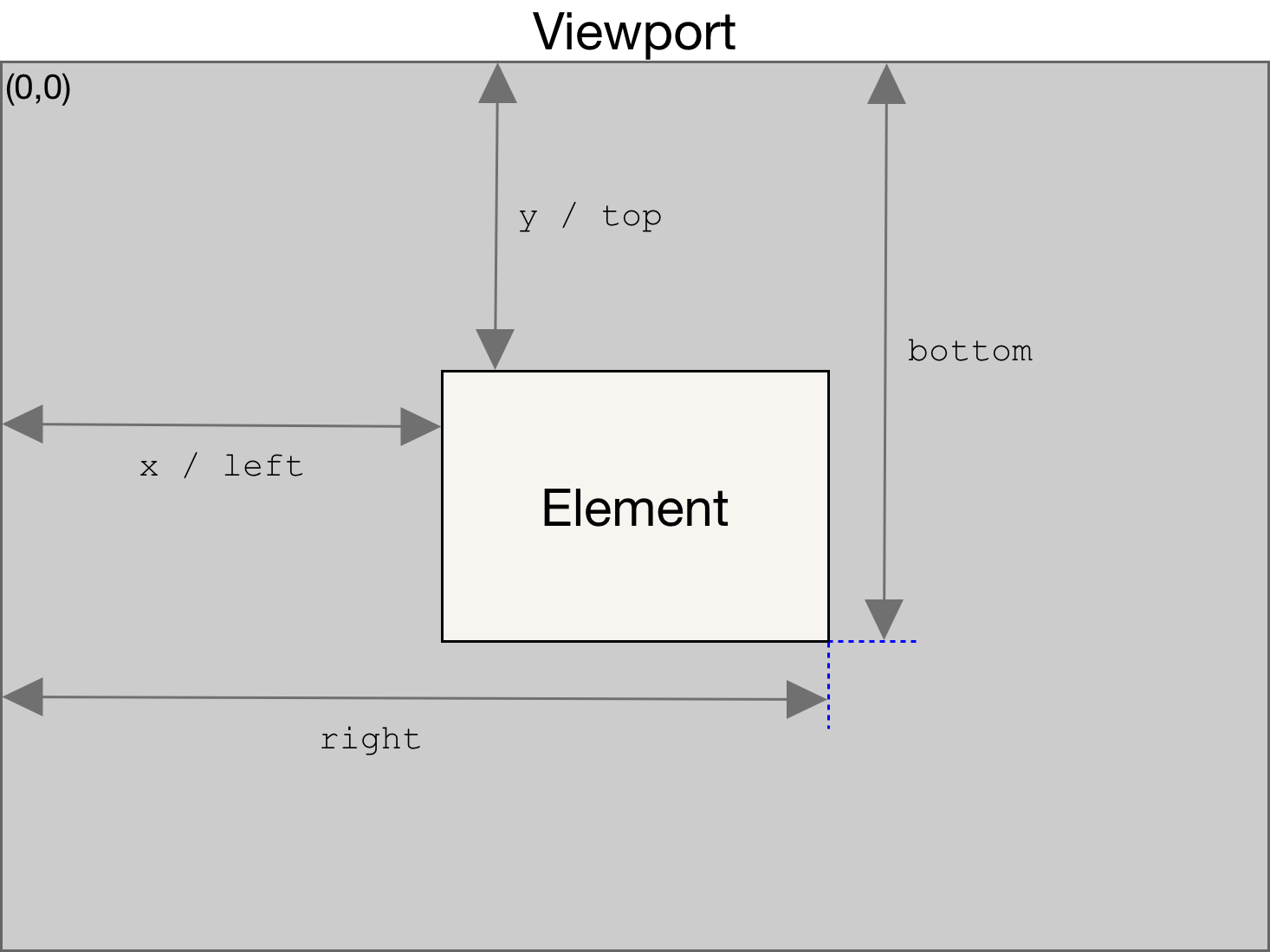
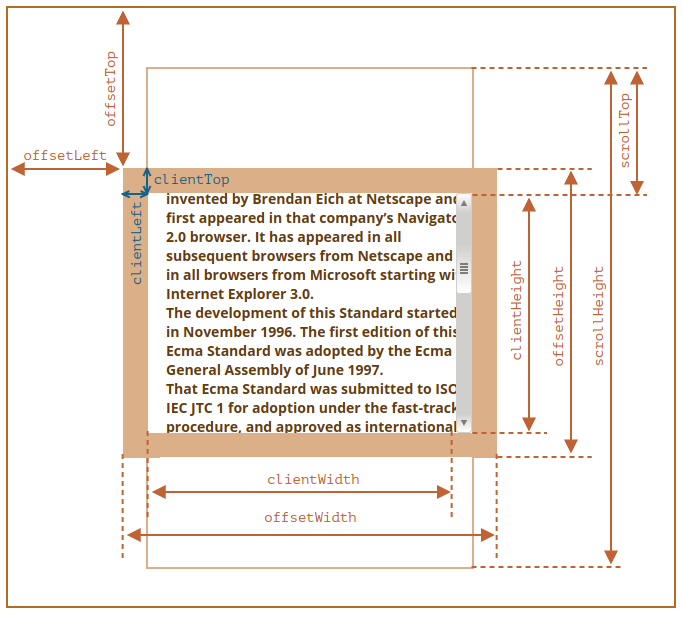
DOM Rect
DOM Width and Height
- outerHeight: 整个浏览器窗口的大小, 包括窗口标题/工具栏/状态栏等.
- innerHeight: DOM 视口的大小, 包括滚动条.
- offsetHeight: 整个可视区域大小, 包括 border 和 scrollbar 在内 (content + padding + border).
- clientHeight: 内部可视区域大小 (content + padding).
- scrollHeight: 元素内容的高度, 包括溢出部分.
// const supportInnerWidth = window.innerWidth !== undefined;
// const supportInnerHeight = window.innerHeight !== undefined;
// const isCSS1Compat = (document.compatMode || '') === 'CSS1Compat';
const width
= window.innerWidth
|| document.documentElement.clientWidth
|| document.body.clientWidth
const height
= window.innerHeight
|| document.documentElement.clientHeight
|| document.body.clientHeight
// 缩放到 100×100
window.resizeTo(100, 100)
// 缩放到 200×150
window.resizeBy(100, 50)
// 缩放到 300×300
window.resizeTo(300, 300)
In case of transforms, the offsetWidth and offsetHeight returns the layout width and height (all the same), while getBoundingClientRect() returns the rendering width and height.
getBoundingClientRect:
function isElementInViewport(el) {
const { top, height, left, width } = el.getBoundingClientRect()
const w
= window.innerWidth
|| document.documentElement.clientWidth
|| document.body.clientWidth
const h
= window.innerHeight
|| document.documentElement.clientHeight
|| document.body.clientHeight
return top <= h && top + height >= 0 && left <= w && left + width >= 0
}
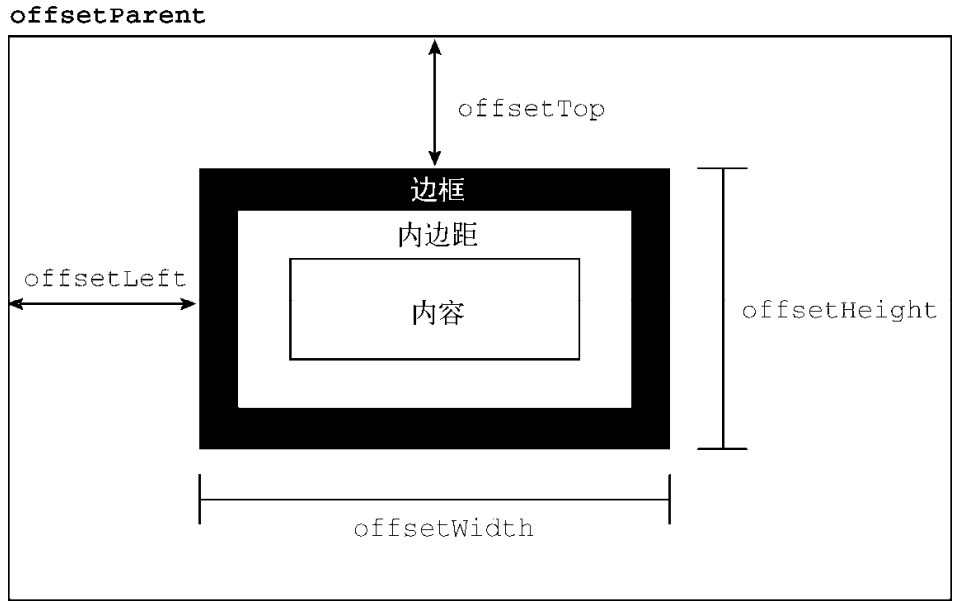
DOM Left and Top
- offsetLeft/offsetTop: 表示该元素的左上角 (边框外边缘) 与已定位的父容器 (offsetParent 对象) 左上角的距离.
- clientLeft/clientTop:
表示该元素 padding 至 margin 的距离,
始终等于
.getComputedStyle()返回的border-left-width/border-top-width. - scrollLeft/scrollTop: 元素滚动条位置, 被隐藏的内容区域左侧/上方的像素位置.
function getElementLeft(element) {
let actualLeft = element.offsetLeft
let current = element.offsetParent
while (current !== null) {
actualLeft += current.offsetLeft
current = current.offsetParent
}
return actualLeft
}
function getElementTop(element) {
let actualTop = element.offsetTop
let current = element.offsetParent
while (current !== null) {
actualTop += current.offsetTop
current = current.offsetParent
}
return actualTop
}
// 把窗口移动到左上角
window.moveTo(0, 0)
// 把窗口向下移动 100 像素
window.moveBy(0, 100)
// 把窗口移动到坐标位置 (200, 300)
window.moveTo(200, 300)
// 把窗口向左移动 50 像素
window.moveBy(-50, 0)
DOM Scroll Size
- scrollLeft/scrollX/PageXOffset: 元素内容向右滚动了多少像素, 如果没有滚动则为 0.
- scrollTop/scrollY/pageYOffset: 元素内容向上滚动了多少像素, 如果没有滚动则为 0.
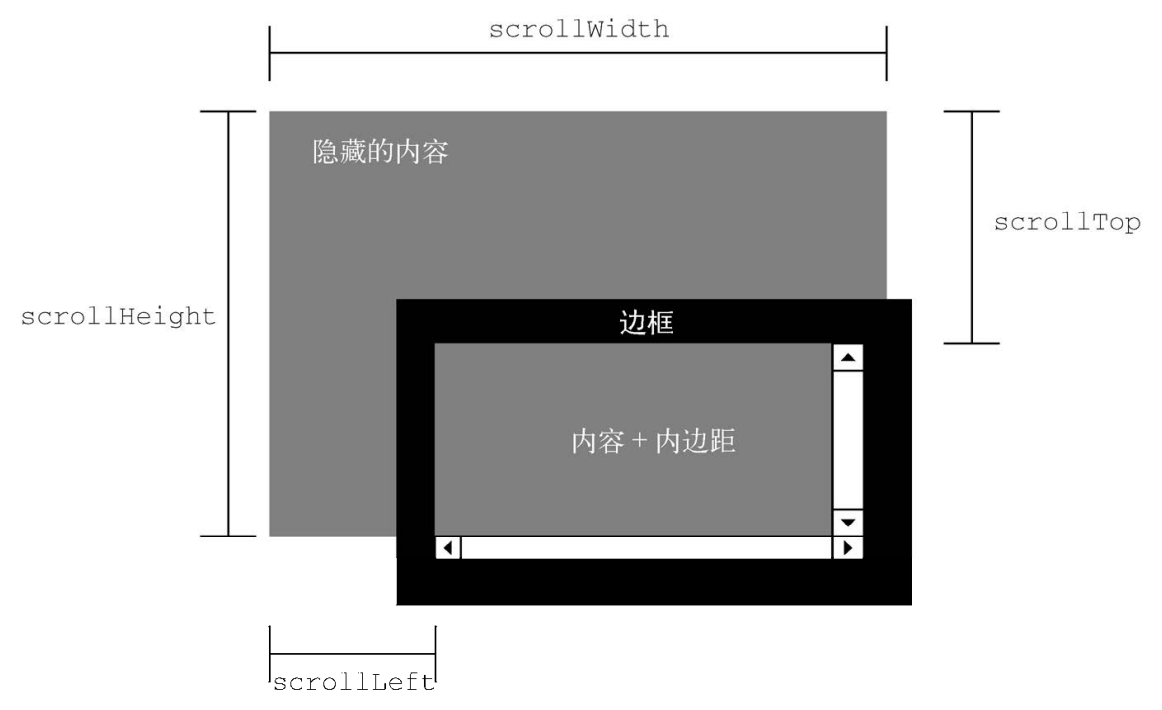
// const supportPageOffset = window.pageXOffset !== undefined;
// const isCSS1Compat = (document.compatMode || '') === 'CSS1Compat';
const x
= window.pageXOffset
|| document.documentElement.scrollLeft
|| document.body.scrollLeft
const y
= window.pageYOffset
|| document.documentElement.scrollTop
|| document.body.scrollTop
if (window.innerHeight + window.pageYOffset === document.body.scrollHeight)
console.log('Scrolled to Bottom!')
// 相对于当前视口向下滚动 100 像素
window.scrollBy(0, 100)
// 相对于当前视口向右滚动 40 像素
window.scrollBy(40, 0)
// 滚动到页面左上角
window.scrollTo(0, 0)
// 滚动到距离屏幕左边及顶边各 100 像素的位置
window.scrollTo(100, 100)
// 正常滚动
window.scrollTo({
left: 100,
top: 100,
behavior: 'auto',
})
// 平滑滚动
window.scrollTo({
left: 100,
top: 100,
behavior: 'smooth',
})
document.forms[0].scrollIntoView() // 窗口滚动后, 元素底部与视口底部对齐.
document.forms[0].scrollIntoView(true) // 窗口滚动后, 元素顶部与视口顶部对齐.
document.forms[0].scrollIntoView({ block: 'start' })
document.forms[0].scrollIntoView({ behavior: 'smooth', block: 'start' })
DOM Observer
Intersection Observer
// <img class="lzy_img" src="lazy_img.jpg" data-src="real_img.jpg" />
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () => {
const imageObserver = new IntersectionObserver((entries, imgObserver) => {
entries.forEach((entry) => {
if (entry.isIntersecting) {
const lazyImage = entry.target
console.log('Lazy loading ', lazyImage)
lazyImage.src = lazyImage.dataset.src
// only load image once
lazyImage.classList.remove('lzy')
imgObserver.unobserve(lazyImage)
}
})
})
const lazyImages = document.querySelectorAll('img.lzy_img')
lazyImages.forEach(lazyImage => imageObserver.observe(lazyImage))
})
Mutation Observer
如果文档中连续插入 1000 个 <li> 元素, 就会连续触发 1000 个插入事件,
执行每个事件的回调函数, 这很可能造成浏览器的卡顿;
Mutation Observer 只会在 1000 个段落都插入结束后才会触发, 且只触发一次.
Mutation Observer 有以下特点:
- 它等待所有脚本任务完成后, 才会运行, 即采用异步方式.
- 它把 DOM 变动记录封装成一个数组进行处理, 而不是一条条地个别处理 DOM 变动.
- 记录队列和回调处理的默认行为是耗尽这个队列, 处理每个 MutationRecord, 然后让它们超出作用域并被垃圾回收.
- MutationObserver 实例拥有被观察目标节点的弱引用, 不会妨碍垃圾回收程序回收目标节点.
- 它即可以观察发生在 DOM 节点的所有变动, 也可以观察某一类变动.
- 被观察子树中的节点 (
{ subtree: true }) 被移出子树之后仍然能够触发变化事件.
const mutationObserver = new MutationObserver((mutations) => {
mutations.forEach((mutation) => {
console.log(mutation)
})
})
// 开始侦听页面的根 HTML 元素中的更改.
mutationObserver.observe(document.documentElement, {
attributes: true,
characterData: true,
childList: true,
subtree: true,
attributeOldValue: true,
characterDataOldValue: true,
})
const target = document.querySelector('#container')
function callback(mutations, observer) {
mutations.forEach((mutation) => {
switch (mutation.type) {
case 'attributes':
// the name of the changed attribute is in
// mutation.attributeName
// and its old value is in mutation.oldValue
// the current value can be retrieved with
// target.getAttribute(mutation.attributeName)
break
case 'childList':
// any added nodes are in mutation.addedNodes
// any removed nodes are in mutation.removedNodes
break
default:
throw new Error('Unsupported mutation!')
}
})
}
const observer = new MutationObserver(callback)
observer.observe(target, {
attributes: true,
attributeFilter: ['foo'], // only observe attribute 'foo'
attributeOldValue: true,
childList: true,
})
const observer = new MutationObserver(mutationRecords =>
console.log(mutationRecords)
)
// 创建两个初始子节点
document.body.appendChild(document.createElement('div'))
document.body.appendChild(document.createElement('span'))
observer.observe(document.body, { childList: true })
// 交换子节点顺序
document.body.insertBefore(document.body.lastChild, document.body.firstChild)
// 发生了两次变化: 第一次是节点被移除, 第二次是节点被添加
// [
// {
// addedNodes: NodeList[],
// attributeName: null,
// attributeNamespace: null,
// oldValue: null,
// nextSibling: null,
// previousSibling: div,
// removedNodes: NodeList[span],
// target: body,
// type: childList,
// },
// {
// addedNodes: NodeList[span],
// attributeName: null,
// attributeNamespace: null,
// oldValue: null,
// nextSibling: div,
// previousSibling: null,
// removedNodes: NodeList[],
// target: body,
// type: "childList",
// }
// ]
XML Namespace
XML 命名空间可以实现在一个格式规范的文档中混用不同的 XML 语言,
避免元素命名冲突 (tagName/localName/namespaceURI):
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>Example XHTML page</title>
</head>
<body>
<s:svg
xmlns:s="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
version="1.1"
viewBox="0 0 100 100"
style="width: 100%; height: 100%"
>
<s:rect x="0" y="0" width="100" height="100" style="fill: red" />
</s:svg>
</body>
</html>
console.log(document.body.isDefaultNamespace('http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml'))
console.log(svg.lookupPrefix('http://www.w3.org/2000/svg')) // "s"
console.log(svg.lookupNamespaceURI('s')) // "http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
const newSvg = document.createElementNS('http://www.w3.org/2000/svg', 'svg')
const newAttr = document.createAttributeNS('http://www.somewhere.com', 'random')
const elems = document.getElementsByTagNameNS(
'http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml',
'*'
)
Network
JSON
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) methods:
const obj = JSON.parse(json)
const json = JSON.stringify(obj)
JSON.stringify(value, filter, space):
Symbol/function/NaN/Infinity/undefined:null/ignored.BitInt: throwTypeError.- Circular reference object: throw
TypeError. toJSONmethod:
const obj = {
name: 'zc',
toJSON() {
return 'return toJSON'
},
}
// return toJSON
console.log(JSON.stringify(obj))
// "2022-03-06T08:24:56.138Z"
JSON.stringify(new Date())
AJAX
AJAX Data Format
| Format | Size (bytes) | Download (ms) | Parse (ms) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verbose XML | 582,960 | 999.4 | 343.1 |
| Verbose JSON-P | 487,913 | 598.2 | 0.0 |
| Simple XML | 437,960 | 475.1 | 83.1 |
| Verbose JSON | 487,895 | 527.7 | 26.7 |
| Simple JSON | 392,895 | 498.7 | 29.0 |
| Simple JSON-P | 392,913 | 454.0 | 3.1 |
| Array JSON | 292,895 | 305.4 | 18.6 |
| Array JSON-P | 292,912 | 316.0 | 3.4 |
| Custom Format (script insertion) | 222,912 | 66.3 | 11.7 |
| Custom Format (XHR) | 222,892 | 63.1 | 14.5 |
AJAX Usage
const XHR = (function () {
const standard = {
createXHR() {
return new XMLHttpRequest()
},
}
const newActionXObject = {
createXHR() {
return new ActionXObject('Msxml12.XMLHTTP')
},
}
const oldActionXObject = {
createXHR() {
return new ActionXObject('Microsoft.XMLHTTP')
},
}
// 根据兼容性返回对应的工厂对象
// 此立即函数运行一次即可完成兼容性检查, 防止重复检查
if (standard.createXHR()) {
return standard
} else {
try {
newActionXObject.createXHR()
return newActionXObject
} catch (o) {
oldActionXObject.createXHR()
return oldActionXObject
}
}
})()
const request = XHR.createXHR()
// 3rd argument : async mode
request.open('GET', 'example.txt', true)
request.onreadystatechange = function () {
// do something
/*
switch(request.readyState) {
case 0: initialize
case 1: loading
case 2: loaded
case 3: transaction
case 4: complete
}
*/
if (request.readyState === 4) {
const para = document.createElement('p')
const txt = document.createTextNode(request.responseText)
para.appendChild(txt)
document.getElementById('new').appendChild(para)
}
}
request.send(null)
ajax({
url: './TestXHR.aspx', // 请求地址
type: 'POST', // 请求方式
data: { name: 'super', age: 20 }, // 请求参数
dataType: 'json',
success(response, xml) {
// 此处放成功后执行的代码
},
fail(status) {
// 此处放失败后执行的代码
},
})
function ajax(options) {
options = options || {}
options.type = (options.type || 'GET').toUpperCase()
options.dataType = options.dataType || 'json'
const params = formatParams(options.data)
let xhr
// 创建 - 非IE6 - 第一步
if (window.XMLHttpRequest) {
xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
} else {
// IE6及其以下版本浏览器
xhr = new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.XMLHTTP')
}
// 接收 - 第三步
xhr.onreadystatechange = function () {
if (xhr.readyState === 4) {
const status = xhr.status
if (status >= 200 && status < 300)
options.success && options.success(xhr.responseText, xhr.responseXML)
else
options.fail && options.fail(status)
}
}
// 连接 和 发送 - 第二步
if (options.type === 'GET') {
xhr.open('GET', `${options.url}?${params}`, true)
xhr.send(null)
} else if (options.type === 'POST') {
xhr.open('POST', options.url, true)
// 设置表单提交时的内容类型
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded')
xhr.send(params)
}
}
// 格式化参数
function formatParams(data) {
const arr = []
for (const name in data)
arr.push(`${encodeURIComponent(name)}=${encodeURIComponent(data[name])}`)
arr.push(`v=${Math.random()}`.replace('.', ''))
return arr.join('&')
}
function getJSON(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const request = new XMLHttpRequest()
request.open('GET', url)
request.onload = function () {
try {
if (this.status === 200)
resolve(JSON.parse(this.response))
else
reject(new Error(`${this.status} ${this.statusText}`))
} catch (e) {
reject(e.message)
}
}
request.onerror = function () {
reject(new Error(`${this.status} ${this.statusText}`))
}
request.send()
})
}
getJSON('data/sample.json')
.then((ninjas) => {
assert(ninjas !== null, 'Get data')
})
.catch(e => handleError(`Error: ${e}`))
AJAX Cross Origin Request
<!-- HTML -->
<meta http-equiv="Access-Control-Allow-Origin" content="*" />
Response.Headers.Add('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*')
$.ajax({
url: 'http://map.oicqzone.com/gpsApi.php?lat=22.502412986242&lng=113.93832783228',
type: 'GET',
dataType: 'JSONP', // 处理 AJAX 跨域问题.
success(data) {
$('body').append(`Name: ${data}`)
},
})
AJAX Alternatives
client.request(config).client.get(url[, config]).client.delete(url[, config]).client.head(url[, config]).client.options(url[, config]).client.post(url[, data[, config]]).client.put(url[, data[, config]]).client.patch(url[, data[, config]]).client.getUri([config]).
const client = axios.create({
baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/',
timeout: 1000,
headers: { 'X-Custom-Header': 'foobar' },
})
// Add a request interceptor
client.interceptors.request.use(
(config) => {
// Do something before request is sent.
return config
},
(error) => {
// Do something with request error.
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
client.interceptors.response.use(
(response) => {
// Any status code that lie within the range of 2xx trigger this function.
// Do something with response data.
return response
},
(error) => {
// Any status codes that falls outside the range of 2xx trigger this function.
// Do something with response error.
return Promise.reject(error)
}
)
Fetch
- GET: read resources.
- POST: create resources.
- PUT: fully update resources.
- PATCH: partially update resources.
- DELETE: delete resources.
Fetch Basis Usage
const response = await fetch('/api/names', {
headers: {
Accept: 'application/json',
},
})
const response = await fetch('/api/names', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify(object),
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
})
Fetch Form Data
const imageFormData = new FormData()
const imageInput = document.querySelector('input[type="file"][multiple]')
const imageFiles = imageInput.files
for (const file of imageFiles)
imageFormData.append('image', file)
fetch('/img-upload', {
method: 'POST',
body: imageFormData,
})
Fetch Aborting
const abortController = new AbortController()
fetch('wikipedia.zip', { signal: abortController.signal }).catch(() =>
console.log('Aborted!')
)
// 10 毫秒后中断请求
setTimeout(() => abortController.abort(), 10)
Fetch Objects API
const myHeaders = new Headers()
myHeaders.append('Content-Type', 'text/xml')
myHeaders.get('Content-Type') // should return 'text/xml'
const request = new Request('/api/names', {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify(object),
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
})
const response = await fetch(request)
fetch('//foo.com').then(console.log)
// Response {
// body: (...)
// bodyUsed: false
// headers: Headers {}
// ok: true
// redirected: false
// status: 200
// statusText: "OK"
// type: "basic"
// url: "https://foo.com/"
// }
fetch('//foo.com/redirect-me').then(console.log)
// Response {
// body: (...)
// bodyUsed: false
// headers: Headers {}
// ok: true
// redirected: true
// status: 200
// statusText: "OK"
// type: "basic"
// url: "https://foo.com/redirected-url/"
// }
fetch('//foo.com/does-not-exist').then(console.log)
// Response {
// body: (...)
// bodyUsed: false
// headers: Headers {}
// ok: false
// redirected: true
// status: 404
// statusText: "Not Found"
// type: "basic"
// url: "https://foo.com/does-not-exist/"
// }
fetch('//foo.com/throws-error').then(console.log)
// Response {
// body: (...)
// bodyUsed: false
// headers: Headers {}
// ok: false
// redirected: true
// status: 500
// statusText: "Internal Server Error"
// type: "basic"
// url: "https://foo.com/throws-error/"
// }
Fetch Streaming
Request/Response body (ReadableStream) methods:
text().json().formData().arrayBuffer().blob().bodyUsed: 布尔值, 表示ReadableStream是否已摄受 (disturbed).
fetch('https://fetch.spec.whatwg.org/')
.then(response => response.body)
.then((body) => {
const reader = body.getReader()
function processNextChunk({ value, done }) {
if (done)
return
console.log(value)
return reader.read().then(processNextChunk)
}
return reader.read().then(processNextChunk)
})
// { value: Uint8Array{}, done: false }
// { value: Uint8Array{}, done: false }
// { value: Uint8Array{}, done: false }
// ...
fetch('https://fetch.spec.whatwg.org/')
.then(response => response.body)
.then(async (body) => {
const reader = body.getReader()
while (true) {
const { value, done } = await reader.read()
if (done)
break
console.log(value)
}
})
// { value: Uint8Array{}, done: false }
// { value: Uint8Array{}, done: false }
// { value: Uint8Array{}, done: false }
// ...
fetch('https://fetch.spec.whatwg.org/')
.then(response => response.body)
.then(async (body) => {
const reader = body.getReader()
const asyncIterable = {
[Symbol.asyncIterator]() {
return {
next() {
return reader.read()
},
}
},
}
for await (const chunk of asyncIterable)
console.log(chunk)
})
// { value: Uint8Array{}, done: false }
// { value: Uint8Array{}, done: false }
// { value: Uint8Array{}, done: false }
// ...
async function* streamGenerator(stream) {
const reader = stream.getReader()
try {
while (true) {
const { value, done } = await reader.read()
if (done)
break
yield value
}
} finally {
reader.releaseLock()
}
}
const decoder = new TextDecoder()
fetch('https://fetch.spec.whatwg.org/')
.then(response => response.body)
.then(async (body) => {
for await (const chunk of streamGenerator(body))
console.log(decoder.decode(chunk, { stream: true }))
})
// <!doctype html><html lang="en"> ...
// whether a <a data-link-type="dfn" href="#concept-header" ...
// result to <var>rangeValue</var>. ...
// ...
fetch('https://fetch.spec.whatwg.org/')
.then(response => response.body)
.then((body) => {
const reader = body.getReader()
// 创建第二个流
return new ReadableStream({
async start(controller) {
try {
while (true) {
const { value, done } = await reader.read()
if (done)
break
// 将主体流的块推到第二个流
controller.enqueue(value)
}
} finally {
controller.close()
reader.releaseLock()
}
},
})
})
.then(secondaryStream => new Response(secondaryStream))
.then(response => response.text())
.then(console.log)
// <!doctype html><html lang="en"><head><meta charset="utf-8"> ...
RESTful
- Client/Server architecture.
- Stateless.
- Cacheable.
- Layer system.
- Code via need.
- Isomorphic interface.
- Design reference.
Server-Sent Events
const source = new EventSource('/path/to/stream-url')
source.onopen = function () {}
source.onerror = function () {}
source.addEventListener('foo', (event) => {
processFoo(event.data)
})
source.addEventListener('ping', (event) => {
processPing(JSON.parse(event.data).time)
})
source.onmessage = function (event) {
log(event.id, event.data)
if (event.id === 'CLOSE')
source.close()
}
WebSocket
WebSocket Message Header
Request Header:
GET /chat HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
Upgrade: websocket
Connection: Upgrade
Sec-WebSocket-Key: 16-byte, base64 encoded
Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13
Sec-Websocket-Protocol: protocol [,protocol]*
Sec-Websocket-Extension: extension [,extension]*
Response Header:
HTTP/1.1 101 "Switching Protocols" or other description
Upgrade: websocket
Connection: Upgrade
Sec-WebSocket-Accept: 20-byte, MD5 hash in base64
Sec-Websocket-Protocol: protocol [,protocol]*
Sec-Websocket-Extension: extension [,extension]*
WebSocket Extensions
WebSocket 存在与 HTTP/1.1 类似的性能瓶颈: 队头阻塞, 无法多路复用.
WebSocket 规范允许对协议进行扩展, 数据格式和 WebSocket 协议的语义可以通过新的操作码和数据字段扩展:
- 多路复用扩展 (WebSocket Multiplexing Extension):
使用
信道 ID扩展每个 WebSocket 帧, 实现多个虚拟的 WebSocket 信道共享一个 TCP 连接. - 压缩扩展 (WebSocket Compression Extension): 给 WebSocket 协议增加了压缩功能.
WebSocket Basic Usage
通信功能:
data:string.ArrayBuffer.Blob.
readyState:WebSocket.OPENING:0, 连接正在建立.WebSocket.OPEN:1, 连接已经建立.WebSocket.CLOSING:2, 连接正在关闭.WebSocket.CLOSE:3, 连接已经关闭.
function WebSocketTest() {
if ('WebSocket' in window) {
alert('WebSocket is supported by your Browser!')
// Let us open a web socket
const ws = new WebSocket('ws://localhost:9998/echo')
ws.onopen = function () {
// WebSocket is connected, send data using send()
ws.send('Message to send')
alert('Message is sent...')
}
ws.onmessage = function (event) {
const receivedMessage = event.data
alert('Message is received...')
}
ws.onclose = function (event) {
// websocket is closed.
console.log(
`As clean? ${event.wasClean} Code=${event.code} Reason=${event.reason}`
)
}
ws.onerror = function () {
alert('Connection error.')
}
} else {
// The browser doesn't support WebSocket
alert('WebSocket NOT supported by your Browser!')
}
}
WebSocket HeartBeat Mechanism
连接终止时, WebSocket 不会自动恢复, 需要自己实现, 通常为了保持连接状态, 需要增加心跳机制.
每隔一段时间会向服务器发送一个数据包, 告诉服务器自己 Alive, 服务器端如果 Alive, 就会回传一个数据包给客户端. 主要在一些长时间连接的应用场景需要考虑心跳机制及重连机制, 以保证长时间的连接及数据交互.
WebSocket Performance
- 使用安全 WebSocket (基于 TLS 的 WSS) 实现可靠的部署, 绕过中间代理.
- 密切关注腻子脚本的性能.
- 利用子协议协商确定应用协议.
- 优化二进制净荷以最小化传输数据.
- 考虑压缩 UTF-8 内容以最小化传输数据.
- 设置正确的二进制类型以接收二进制净荷.
- 监控客户端缓冲数据的量.
- 切分应用消息以避免队首阻塞.
- 合用的情况下利用其他传输机制.
- 对于无线设备, 注意节能: 消除周期性无效数据, 减少冗余数据, 消除不必要的长连接.
WebSocket Reference
WebRTC
Web Real-Time Communication
Web Real-Time Communication (Web 实时通信, WebRTC) 由一组标准, 协议和 JavaScript API 组成, 用于实现浏览器之间 (端到端, P2P) 的音频/视频/数据共享:
- MediaStream.
- RTCPeerConnection:
- 管理穿透 NAT 的完整 ICE 工作流.
- 发送自动 (STUN) 持久化信号.
- 跟踪本地流.
- 跟踪远程流.
- 按需触发自动流协商.
- 生成连接提议, 接收应答, 允许查询连接的当前状态等.
- RTCDataChannel: DataChannel API 用于实现端到端之间的任意应用数据交换 (端到端交换版本的 WebSocket).
WebRTC Layer Protocol
- WebRTC 使用 UDP 作为传输层协议: 低延迟和及时性才是关键.
- ICE: Interactive Connectivity Establishment (RFC 5245).
- STUN: Session Traversal Utilities for NAT (RFC 5389).
- TURN: Traversal Using Relays around NAT (RFC 5766).
- SDP: Session Description Protocol (RFC 4566).
- DTLS: Datagram Transport Layer Security (RFC 6347).
- SCTP: Stream Control Transport Protocol (RFC 4960).
- SRTP: Secure Real-Time Transport Protocol (RFC 3711).
WebRTC Basic Usage
const ice = {
iceServers: [
{ url: 'stun:stun.l.google.com:19302' },
{ url: 'turn:user@turnserver.com', credential: 'pass' },
],
}
const signalingChannel = new SignalingChannel()
const pc = new RTCPeerConnection(ice)
navigator.getUserMedia({ audio: true }, getStream, logError)
function getStream(evt) {
pc.addstream(evt.stream)
const localVideo = document.querySelector('#local-video')
localVideo.src = window.URL.createObjectURL(evt.stream)
pc.createOffer((offer) => {
pc.setLocalDescription(offer)
signalingChannel.send(offer.sdp)
})
}
pc.onicecandidate = function (evt) {
if (evt.candidate)
signalingChannel.send(evt.candidate)
}
pc.oniceconnectionstatechange = function (evt) {
logStatus(`ICE connection state change: ${evt.target.iceConnectionState}`)
}
pc.onaddstream = function (evt) {
const remoteVideo = document.querySelector('#remote-video')
remoteVideo.src = window.URL.createObjectURL(evt.stream)
}
signalingChannel.onmessage = function (msg) {
if (msg.candidate)
pc.addIceCandidate(msg.candidate)
}
WebRTC Performance
- 发信服务:
- 使用低延迟传输机制.
- 提供足够的容量.
- 建立连接后, 考虑使用 DataChannel 发信.
- 防火墙和 NAT 穿透:
- 初始化 RTCPeerConnection 时提供 STUN 服务器.
- 尽可能使用增量 ICE, 虽然发信次数多, 但建立连接速度快.
- 提供 STUN 服务器, 以备端到端连接失败后转发数据.
- 预计并保证 TURN 转发时容量足够用.
- 数据分发:
- 对于大型多方通信, 考虑使用超级节点或专用的中间设备.
- 中间设备在转发数据前, 考虑先对其进行优化或压缩.
- 数据效率:
- 对音频和视频流指定适当的媒体约束.
- 优化通过 DataChannel 发送的二进制净荷.
- 考虑压缩通过 DataChannel 发送的 UTF-8 数据.
- 监控 DataChannel 缓冲数据的量, 同时注意适应网络条件变化.
- 交付及可靠性:
- 使用乱序交付避免队首阻塞.
- 如果使用有序交付, 把消息大小控制到最小, 以降低队首阻塞的影响.
- 发送小消息 (小于 1150 字节), 以便将分段应用消息造成的丢包损失降至最低.
- 对部分可靠交付:
- 设置适当的重传次数和超时间隔.
- 正确的设置取决于消息大小, 应用数据类型, 端与端之间的延迟.
WebRTC Reference
Web Animations
Keyframe Effect API
KeyframeEffect:
const rabbitDownKeyframes = new KeyframeEffect(
whiteRabbit, // element to animate
[
{ transform: 'translateY(0%)' }, // keyframe
{ transform: 'translateY(100%)' }, // keyframe
],
{ duration: 3000, fill: 'forwards' } // keyframe options
)
const rabbitDownAnimation = new Animation(
rabbitDownKeyFrames,
document.timeline
)
whiteRabbit.addEventListener('click', downHandler)
function downHandler() {
rabbitDownAnimation.play()
whiteRabbit.removeEventListener('click', downHandler)
}
Animation API
animation.currentTime.animation.playState.animation.effect.animation.pause()/play()/reverse()/finish()/cancel().
animation.currentTime = animation.effect.getComputedTiming().duration / 2
function currentTime(time = 0) {
animations.forEach((animation) => {
if (typeof animation.currentTime === 'function')
animation.currentTime(time)
else
animation.currentTime = time
})
}
function createPlayer(animations) {
return Object.freeze({
play() {
animations.forEach(animation => animation.play())
},
pause() {
animations.forEach(animation => animation.pause())
},
currentTime(time = 0) {
animations.forEach(animation => (animation.currentTime = time))
},
})
}
Animate API
element.animate:
const animationKeyframes = [
{
transform: 'rotate(0)',
color: '#000',
},
{
color: '#431236',
offset: 0.3,
},
{
transform: 'rotate(360deg)',
color: '#000',
},
]
const animationTiming = {
duration: 3000,
iterations: Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY,
}
const animation = document
.querySelector('alice')
.animate(animationKeyframes, animationTiming)
Web Animations Reference
- Using Web Animations API.
Web Canvas
Canvas Basic Usage
- Path2D 对象.
- 绘制路径:
beginPath()->draw()->closePath(). - 绘制样式: 颜色/渐变/变换/阴影.
- 绘制图形:
fill/stroke/clip. - 绘制文字:
font/fillText()/measureText().
const context = canvas.getContext('2d')
// 根据参数画线
function drawLine(fromX, fromY, toX, toY) {
context.moveTo(fromX, fromY)
context.lineTo(toX, toY)
context.stroke()
}
// 根据参数画圆
function drawCircle(x, y, radius, color) {
context.fillStyle = color
context.beginPath()
context.arc(x, y, radius, 0, Math.PI * 2, true)
context.closePath()
context.fill()
context.stroke()
}
// 改变 canvas 中图形颜色
function changeColor(color) {
context.fillStyle = color
context.fill()
}
<canvas width="600" height="300"></canvas>
<script>
const cx = document.querySelector('canvas').getContext('2d')
function branch(length, angle, scale) {
cx.fillRect(0, 0, 1, length)
if (length < 8) return
cx.save()
cx.translate(0, length)
cx.rotate(-angle)
branch(length * scale, angle, scale)
cx.rotate(2 * angle)
branch(length * scale, angle, scale)
cx.restore()
}
cx.translate(300, 0)
branch(60, 0.5, 0.8)
</script>
Canvas Game Loop
For all objects:
- constructor:
position{x, y},speed{x, y},size{x, y} - update(deltaTime): change position or speed
- draw(ctx): use canvas api and object properties (position/size) to render objects
const canvas = document.getElementById('gameScreen')
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d')
const GAME_WIDTH = 800
const GAME_HEIGHT = 600
const game = new Game(GAME_WIDTH, GAME_HEIGHT)
let lastTime = 0
function gameLoop(timestamp) {
const deltaTime = timestamp - lastTime
lastTime = timestamp
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, GAME_WIDTH, GAME_HEIGHT)
game.update(deltaTime)
game.draw(ctx)
requestAnimationFrame(gameLoop)
}
requestAnimationFrame(gameLoop)
Canvas Performance
Canvas buffer:
frontCanvasContext.drawImage(bufferCanvas, 0, 0)
- multiple canvas: top layer, background layer, interactive layer
- disable alpha path
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d', { alpha: false })
Offscreen canvas and web workers:
transferControlToOffscreen method:
// index.js
const offscreenCanvas = document.querySelector('#frame2')
const offscreen = offscreenCanvas.transferControlToOffscreen()
const worker = new Worker('./worker.js')
worker.postMessage({ canvas: offscreen }, [offscreen])
// worker.js
onmessage = function (event) {
canvas = event.data.canvas
context = canvas.getContext('2d')
}
OffscreenCanvas in service workers:
// Create reusable canvas
const offscreen = new OffscreenCanvas(512, 512)
const context = offscreen.getContext('2d')
// eslint-disable-next-line no-restricted-globals -- Service worker.
self.addEventListener('fetch', (ev) => {
// Only handle image requests
const url = new URL(ev.request.url)
if (url.pathname.startsWith('/artwork/'))
ev.respondWith(artwork(ev))
})
async function artwork(ev) {
const cache = await caches.open('artwork')
// 1. Return from cache
let response = await cache.match(ev.request)
if (response)
return response
// 2. Or fetch from network
response = await fetch(ev.request)
if (!response.ok || response.status !== 200)
return response
// 3. Use canvas to resize
let blob = await response.blob()
context.drawImage(await createImageBitmap(blob), 0, 0, 512, 512)
blob = await offscreen.convertToBlob({ type: 'image/png' })
// 4. Create new headers
const headers = new Headers(response.headers)
headers.set('content-type', blob.type)
headers.set('content-length', blob.size)
// 5. Create new response
const { status, statusText } = response
response = new Response(await blob.arrayBuffer(), {
status,
statusText,
headers
})
await cache.put(ev.request, response.clone())
return response
}
CSS Houdini Painting API
// checkerboard.js:
// Create a `PaintWorklet`.
class CheckerboardPainter {
static get contextOptions() {
return { alpha: true }
}
/**
* @returns {string[]} any custom properties or regular properties
*/
static get inputProperties() {
return ['--red', '--green', '--blue', '--width', 'height']
}
paint(context, geometry, props) {
const colors = [
props.get('--red').toString(),
props.get('--green').toString(),
props.get('--blue').toString(),
]
const size = Number.parseInt(props.get('--width'))
for (let y = 0; y < geometry.height / size; y++) {
for (let x = 0; x < geometry.width / size; x++) {
const color = colors[(x + y) % colors.length]
context.beginPath()
context.fillStyle = color
context.rect(x * size, y * size, size, size)
context.fill()
}
}
}
}
// Register our class under a specific name
registerPaint('checkerboard', CheckerboardPainter)
<!-- Load a `PaintWorklet`. -->
<script>
if ('paintWorklet' in CSS) {
CSS.paintWorklet.addModule('checkerboard.js')
}
</script>
<!-- Use a `PaintWorklet`. -->
<style>
textarea {
background-image: paint(checkerboard);
}
</style>
<textarea></textarea>
Canvas Reference
- Canvas API
- Canvas Tutorial
- Canvas Deep Dive
- Canvas Cheat Sheet
- Canvas Performance
- Canvas Real World Case
Web Audio
Oscillator
-3 -1 1 4 6 9 11
-4 -2 0 2 3 5 7 8 10 12
.___________________________________________________________________________.
: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | :
: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | :
: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | :
<-: |_| | |_| |_| | |_| |_| |_| | |_| |_| | |_| |_| |_| | |_| |_| :->
: | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | :
: A | B | C | D | E | F | G | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | A | B | C | D | E :
:___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___|___:
^ ^ ^ ^ ^
220 Hz 440 Hz 523.25 Hz 880 Hz 1174.65 Hz
(-1 Octave) (middle A) (+1 Octave)
const audioContext = new AudioContext()
const baseFrequency = 440
const getNoteFreq = (base, pitch) => base * 2 ** (pitch / 12)
// oscillator.frequency.value = getNoteFreq(440, 7);
const getNoteDetune = pitch => pitch * 100
// oscillator.detune.value = getNoteDetune(7);
function play(type, delay, pitch, duration) {
const oscillator = audioContext.createOscillator()
oscillator.connect(audioContext.destination)
oscillator.type = type
oscillator.detune.value = getNoteDetune(pitch)
const startTime = audioContext.currentTime + delay
const stopTime = startTime + duration
oscillator.start(startTime)
oscillator.stop(stopTime)
}
Music Data
const sampleSize = 1024 // number of samples to collect before analyzing data
const audioUrl = 'viper.mp3'
let audioData = null
let audioPlaying = false
const audioContext = new AudioContext()
const sourceNode = audioContext.createBufferSource()
const analyserNode = audioContext.createAnalyser()
const javascriptNode = audioContext.createScriptProcessor(sampleSize, 1, 1)
// Create the array for the data values
const amplitudeArray = new Uint8Array(analyserNode.frequencyBinCount)
// Now connect the nodes together
sourceNode.connect(audioContext.destination)
sourceNode.connect(analyserNode)
analyserNode.connect(javascriptNode)
javascriptNode.connect(audioContext.destination)
// setup the event handler that is triggered
// every time enough samples have been collected
// trigger the audio analysis and draw the results
javascriptNode.onaudioprocess = function () {
// get the Time Domain data for this sample
analyserNode.getByteTimeDomainData(amplitudeArray)
// draw the display if the audio is playing
// if (audioPlaying === true) {
// requestAnimFrame(drawTimeDomain);
// }
}
// Load the audio from the URL via AJAX and store it in global variable audioData
// Note that the audio load is asynchronous
function loadSound(url) {
fetch(url)
.then((response) => {
audioContext.decodeAudioData(response, (buffer) => {
audioData = buffer
playSound(audioData)
})
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error)
})
}
// Play the audio and loop until stopped
function playSound(buffer) {
sourceNode.buffer = buffer
sourceNode.start(0) // Play the sound now
sourceNode.loop = true
audioPlaying = true
}
function stopSound() {
sourceNode.stop(0)
audioPlaying = false
}
Audio Bar Chart
const WIDTH = this.canvas.clientWidth
const HEIGHT = this.canvas.clientHeight
this.analyserNode.fftSize = 256
const bufferLengthAlt = this.analyserNode.frequencyBinCount
const dataArrayAlt = new Uint8Array(bufferLengthAlt)
this.ctx.clearRect(0, 0, WIDTH, HEIGHT)
function draw() {
const drawVisual = requestAnimationFrame(draw)
this.analyserNode.getByteFrequencyData(dataArrayAlt)
this.ctx.fillStyle = 'rgb(255, 255, 255)'
this.ctx.fillRect(0, 0, WIDTH, HEIGHT)
const barWidth = (WIDTH / bufferLengthAlt) * 2.5
let barHeight
let x = 0
for (let i = 0; i < bufferLengthAlt; i++) {
barHeight = dataArrayAlt[i]
this.ctx.fillStyle = `rgb(${barHeight + 100},15,156)`
this.ctx.fillRect(x, HEIGHT - barHeight / 2, barWidth, barHeight / 2)
x += barWidth + 1
}
}
draw()
Media Session
Web Storage
- Cookie for session state.
- DOM storage for Web Component state.
- Web Storage for simple UI options (dark mode, sidebar size, etc.).
- IndexedDB for large binary objects and data dumps.
- Cache API for offline and quick file access.
- JavaScript variables for everything else.
Cookie
name=value..expires=expiration_time.path=domain_path.domain=domain_name.secure.
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-type: text/html
Set-Cookie: name=value; expires=Mon, 22-Jan-07 07:10:24 GMT; domain=.foo.com
Other-header: other-header-value
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-type: text/html
Set-Cookie: name=value; domain=.foo.com; path=/; secure
Other-header: other-header-value
class CookieUtil {
static get(name) {
const cookieName = `${encodeURIComponent(name)}=`
const cookieStart = document.cookie.indexOf(cookieName)
let cookieValue = null
if (cookieStart > -1) {
let cookieEnd = document.cookie.indexOf(';', cookieStart)
if (cookieEnd === -1)
cookieEnd = document.cookie.length
cookieValue = decodeURIComponent(
document.cookie.substring(cookieStart + cookieName.length, cookieEnd)
)
}
return cookieValue
}
static set(name, value, { expires, path, domain, secure }) {
let cookieText = `${encodeURIComponent(name)}=${encodeURIComponent(value)}`
if (expires instanceof Date)
cookieText += `; expires=${expires.toGMTString()}`
if (path)
cookieText += `; path=${path}`
if (domain)
cookieText += `; domain=${domain}`
if (secure)
cookieText += '; secure'
document.cookie = cookieText
}
static unset(name, { path, domain, secure }) {
CookieUtil.set(name, '', new Date(0), path, domain, secure)
}
}
Local Storage
- 协同 Cookie.
- 对于复杂对象的读取与存储,
需要借助
JSON.parse与JSON.stringify. Storageobject:Storage.length.Storage.key().Storage.getItem().Storage.setItem().Storage.removeItem().Storage.clear().
storageevent: 每当Storage对象发生变化时, 都会在文档上触发storage事件.event.domain: 存储变化对应的域.event.key: 被设置或删除的键.event.newValue: 键被设置的新值, 若键被删除则为 null.event.oldValue: 键变化之前的值.
if (!localStorage.getItem('bgColor'))
populateStorage()
else
setStyles()
function populateStorage() {
localStorage.setItem('bgColor', document.getElementById('bgColor').value)
localStorage.setItem('font', document.getElementById('font').value)
localStorage.setItem('image', document.getElementById('image').value)
setStyles()
}
function setStyles() {
const currentColor = localStorage.getItem('bgColor')
const currentFont = localStorage.getItem('font')
const currentImage = localStorage.getItem('image')
document.getElementById('bgColor').value = currentColor
document.getElementById('font').value = currentFont
document.getElementById('image').value = currentImage
htmlElem.style.backgroundColor = `#${currentColor}`
pElem.style.fontFamily = currentFont
imgElem.setAttribute('src', currentImage)
}
IndexDB
class IndexedDB {
constructor(dbName, dbVersion, dbUpgrade) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
this.db = null
if (!('indexedDB' in window))
reject(new Error('Not supported'))
const dbOpen = indexedDB.open(dbName, dbVersion)
if (dbUpgrade) {
dbOpen.onupgradeneeded = (e) => {
dbUpgrade(dbOpen.result, e.oldVersion, e.newVersion)
}
}
dbOpen.onsuccess = () => {
this.db = dbOpen.result
resolve(this)
}
dbOpen.onerror = (e) => {
reject(new Error(`IndexedDB error: ${e.target.errorCode}`))
}
})
}
get(storeName, name) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const transaction = this.db.transaction(storeName, 'readonly')
const store = transaction.objectStore(storeName)
const request = store.get(name)
request.onsuccess = () => {
resolve(request.result)
}
request.onerror = () => {
reject(request.error)
}
})
}
set(storeName, name, value) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const transaction = this.db.transaction(storeName, 'readwrite')
const store = transaction.objectStore(storeName)
store.put(value, name)
transaction.oncomplete = () => {
resolve(true)
}
transaction.onerror = () => {
reject(transaction.error)
}
})
}
}
export class State {
static dbName = 'stateDB'
static dbVersion = 1
static storeName = 'state'
static DB = null
static target = new EventTarget()
constructor(observed, updateCallback) {
this.updateCallback = updateCallback
this.observed = new Set(observed)
// subscribe `set` event with `updateCallback`
State.target.addEventListener('set', (e) => {
if (this.updateCallback && this.observed.has(e.detail.name))
this.updateCallback(e.detail.name, e.detail.value)
})
}
async dbConnect() {
State.DB
= State.DB
|| (await new IndexedDB(
State.dbName,
State.dbVersion,
(db, oldVersion, newVersion) => {
// upgrade database
switch (oldVersion) {
case 0: {
db.createObjectStore(State.storeName)
break
}
default:
throw new Error('Unsupported version!')
}
}
))
return State.DB
}
async get(name) {
this.observedSet.add(name)
const db = await this.dbConnect()
return await db.get(State.storeName, name)
}
async set(name, value) {
this.observed.add(name)
const db = await this.dbConnect()
await db.set(State.storeName, name, value)
// publish event to subscriber
const event = new CustomEvent('set', { detail: { name, value } })
State.target.dispatchEvent(event)
}
}
const store = db.transaction('users').objectStore('users')
const index = store.createIndex('username', 'username', { unique: true })
const range = IDBKeyRange.bound('007', 'ace')
const request = store.openCursor(range, 'next')
const request = index.openCursor(range, 'next')
request.onsuccess = function (event) {
const cursor = event.target.result
if (cursor) {
// 永远要检查
console.log(`Key: ${cursor.key}, Value: ${JSON.stringify(cursor.value)}`)
cursor.continue() // 移动到下一条记录
} else {
console.log('Done!')
}
}
File API
function readFileText(file) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const reader = new FileReader()
reader.addEventListener('load', () => resolve(reader.result))
reader.addEventListener('error', () => reject(reader.error))
reader.readAsText(file)
})
}
function readFileBuffer(file) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const reader = new FileReader()
reader.addEventListener('load', () => resolve(reader.result))
reader.addEventListener('error', () => reject(reader.error))
reader.readAsArrayBuffer(file)
})
}
const fileInput = document.querySelector('fileInput')
for (const file of fileInput.files) {
const text = await readFileText(file)
const buffer = await readFileBuffer(file)
}
Web Payment
async function doPaymentRequest() {
try {
// new PaymentRequest(paymentMethods, paymentDetails);
const request = new PaymentRequest(
[
{
supportedMethods: 'https://bobpay.xyz/pay',
},
],
{
total: {
label: 'total',
amount: { value: '10', currency: 'USD' },
},
}
)
const response = await request.show()
await validateResponse(response)
} catch (err) {
// AbortError, SecurityError
console.error(err)
}
}
async function validateResponse(response) {
try {
const errors = await checkAllValuesAreGood(response)
if (errors.length) {
await response.retry(errors)
return validateResponse(response)
}
await response.complete('success')
} catch (err) {
// Something went wrong…
await response.complete('fail')
}
}
doPaymentRequest()
Web Devices
Web Gamepad
const gamepads = {}
function gamepadHandler(event, connecting) {
// gamepad === navigator.getGamepads()[gamepad.index]
const { gamepad } = event
if (connecting)
gamepads[gamepad.index] = gamepad
else
delete gamepads[gamepad.index]
}
window.addEventListener('gamepadconnected', (e) => {
gamepadHandler(e, true)
})
window.addEventListener('gamepaddisconnected', (e) => {
gamepadHandler(e, false)
})
Web Bluetooth
navigator.bluetooth
.requestDevice({ filters: [{ services: ['health_thermometer'] }] })
.then(device => device.gatt.connect())
.then(server => server.getPrimaryService('health_thermometer'))
.then(service => service.getCharacteristic('measurement_interval'))
.then(characteristic =>
characteristic.getDescriptor('gatt.characteristic_user_description')
)
.then((descriptor) => {
const encoder = new TextEncoder('utf-8')
const userDescription = encoder.encode(
'Defines the time between measurements.'
)
return descriptor.writeValue(userDescription)
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error)
})
Web USB
let device
navigator.usb
.requestDevice({ filters: [{ vendorId: 0x2341 }] })
.then((selectedDevice) => {
device = selectedDevice
return device.open() // Begin a session.
})
.then(() => device.selectConfiguration(1)) // Select configuration for the device.
.then(() => device.claimInterface(2)) // Request exclusive control over interface.
.then(() =>
device.controlTransferOut({
requestType: 'class',
recipient: 'interface',
request: 0x22,
value: 0x01,
index: 0x02,
})
) // Ready to receive data
.then(() => device.transferIn(5, 64)) // Waiting for 64 bytes of data from endpoint.
.then((result) => {
const decoder = new TextDecoder()
console.log(`Received: ${decoder.decode(result.data)}`)
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error(error)
})
Web NFC
const encoder = new TextEncoder()
const data = {
firstName: 'First',
lastName: 'Last',
}
const jsonRecord = {
recordType: 'mime',
mediaType: 'application/json',
data: encoder.encode(JSON.stringify(data)),
}
const imageRecord = {
recordType: 'mime',
mediaType: 'image/png',
data: await(await fetch('icon1.png')).arrayBuffer(),
}
const ndef = new NDEFReader()
await ndef.write({ records: [jsonRecord, imageRecord] })
Web Serial
// Prompt user to select any serial port.
const port = await navigator.serial.requestPort()
// Wait for the serial port to open.
await port.open({ baudRate: 9600 })
// Close a serial port.
await port.close()
const textDecoder = new TextDecoderStream()
const readableStreamClosed = port.readable.pipeTo(textDecoder.writable)
const reader = textDecoder.readable.getReader()
// Listen to data coming from the serial device.
while (true) {
const { value, done } = await reader.read()
if (done) {
// Allow the serial port to be closed later.
reader.releaseLock()
break
}
// value is a string.
console.log(value)
}
const textEncoder = new TextEncoderStream()
const writableStreamClosed = textEncoder.readable.pipeTo(port.writable)
const writer = textEncoder.writable.getWriter()
await writer.write('hello')
Web HID
function waitFor(duration) {
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, duration))
}
// Prompt user to select an Apple Keyboard Backlight device.
const [device] = await navigator.hid.requestDevice({
filters: [{ vendorId: 0x05AC, usage: 0x0F, usagePage: 0xFF00 }],
})
// Wait for the HID connection to open.
await device.open()
// Blink!
const reportId = 1
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
// Turn off
await device.sendFeatureReport(reportId, Uint32Array.from([0, 0]))
await waitFor(100)
// Turn on
await device.sendFeatureReport(reportId, Uint32Array.from([512, 0]))
await waitFor(100)
}